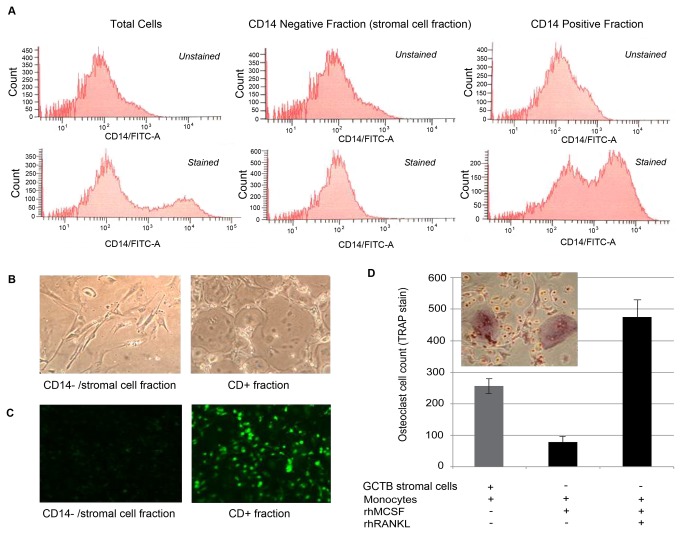
Figure 1. Separation of total GCTB cell digest into stromal and myeloid fractions.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of CD14+ cell population in total dispersed cells, stromal cell fraction and column retained fraction after CD14 negative selection column separation (top row: unstained control; bottom row: FITC-labeled anti-CD14 Ab). (B) Post-column separation phase contrast microscopy demonstrating morphology consistent with GCT stromal cells (left) and a combination of multinucleated giant cells plus monocytic, mononuclear cells (right). (C) CD14 immunofluorescence of cells grown on glass coverslips from the stromal cell (left) and column retained fractions (right). (D) Isolated GCT stromal cells maintain their ability to induce osteoclast formation in co-culture with human peripheral blood monocytes.