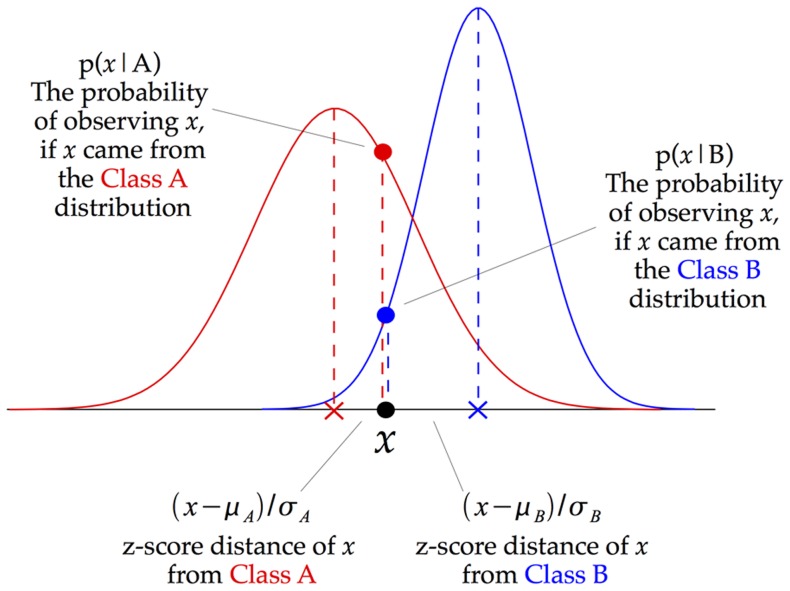
Figure 1. Illustration of how a Gaussian Naive Bayes (GNB) classifier works.
For each data point, the z-score distance between that point and each class-mean is calculated, namely the distance from the class mean divided by the standard deviation of that class. Note that this schematic just shows one dimension, whereas a crucial distinction between GNBs and other classifiers arises only when there is more than one input dimension: the GNB does not model the covariance between dimensions, but other types of classifier do.