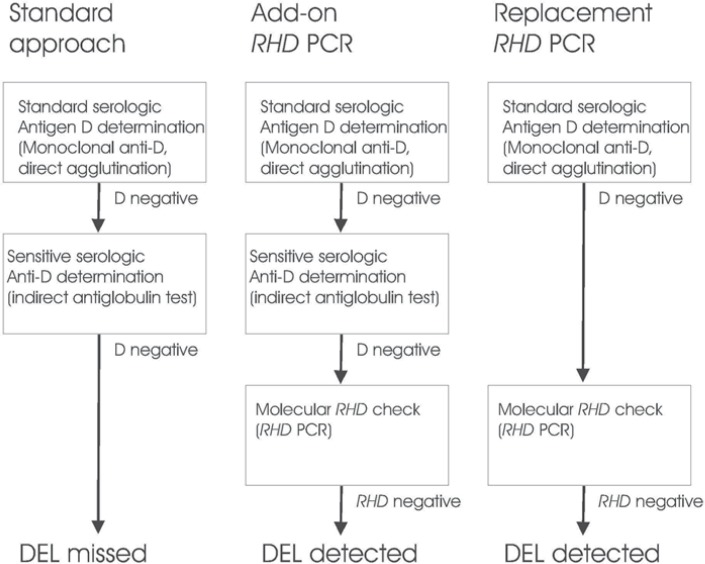
Fig. 1.
Add-on and replacement RHD PCR. Different approaches for the determination of the antigen D status of first time donors are shown. Left: In standard antigen D determination, donors are first tested with a directly agglutinating monoclonal anti-D, and D-negative donors are then checked by the indirect agglutinin test with an oligoclonal anti-D to detect weak D and partial D antigens. DEL are missed by this approach. Middle: DEL may be detected by adding RHD PCR to the standard D determination. This approach eliminates any risk that D-positive donors detectable by the serologie approach are missed, but of cause the cost must be higher than that of the conventional approach. Right: DEL may be also detected by testing donors D-negative by direct agglutination by RHD PCR. This approach is safe, as long as the RHD PCR is devised in a way that weak D and partial D alle-les are detected, too. The cost of this approach may be higher or lower than that of the standard approach, depending on the relative cost of the indirect antiglobulin test and the RHD PCR used.