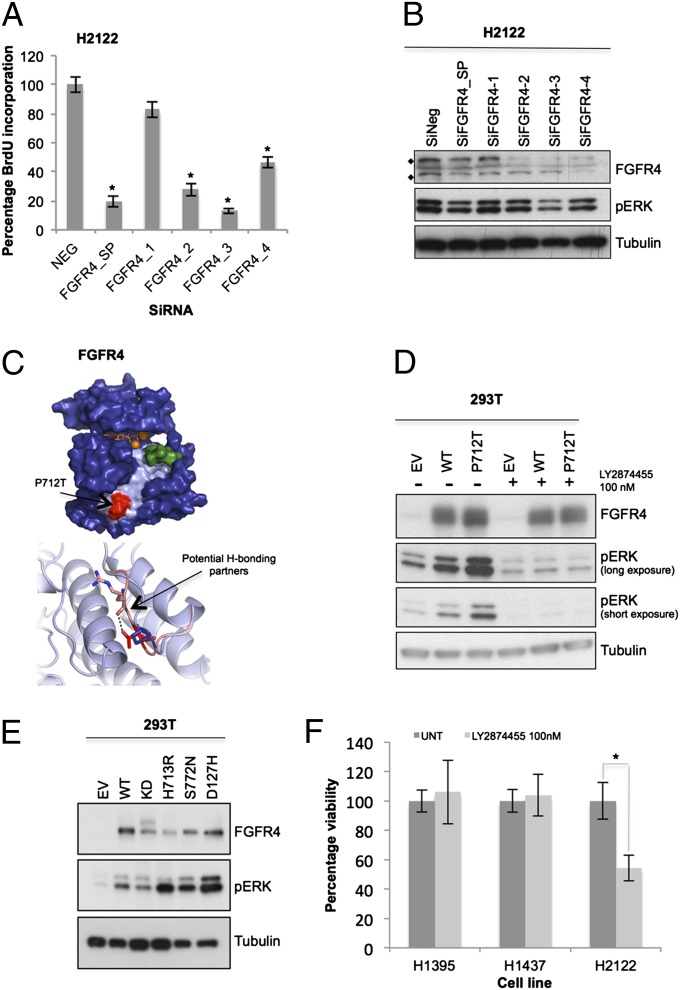
Fig. 4.
FGFR4 is a mutationally activated receptor tyrosine kinase essential for lung cancer cell proliferation. (A) FGFR4 was knocked down in H2122 cells (SMARTpool 100 nM; oligos 1–4, 25 nM). Plates were subjected to BrdU assay or MTT assay (SI Appendix, Fig. S3A), and data were normalized to nontargeting siRNA (NEG). (B) On-target effect of FGFR4 SMARTpool (100 nM) and individual oligos (25 nM) was also verified by Western blotting. Protein lysates were probed for FGFR4 protein level (♦, FGFR4 unmodified at 88 kDa and modified at 125 KDa) and inhibition of downstream signals of pERK compared with the nontargeting siRNA (SiNeg). (C, Upper) Model of the FGFR4 tyrosine kinase domain based on the crystal structure of FGFR2 (PDB ID 2PVF) bound to ATP and magnesium ions (orange sticks and spheres, respectively). Partial substrate (green) is bound into the potential binding pocket (pale blue). P712T mutation site is shown in red. (C, Lower) Potential additional hydrogen-bonding partners of the mutant structure (R670) as pink sticks compared with WT. (D) Empty vector (EV), FGFR4 WT, and P712T mutant were expressed ectopically in 293T cells, with or without treatment with the FGFR inhibitor LY2874455, 30 min before lysis. (E) FGFR4 cancer mutants were also generated and overexpressed in 293T cells for 48 h, compared with empty vector, WT, and kinase-dead K503M (KD). Lysates were collected, and downstream ERK phosphorylation was analyzed by Western blotting. (F) H2122 cells (FGFR4P712T) and H1395 and H1437 (FGFRWT) were treated with FGFR inhibitor and assayed by MTT. Data (n = 9) were normalized to untreated cells (UNT; DMSO, <0.01%). Error bars show SD. P values were calculated by using one-tailed paired Student t test (*P < 0.005 vs. nontargeting siRNA or untreated).