Fig. 3.
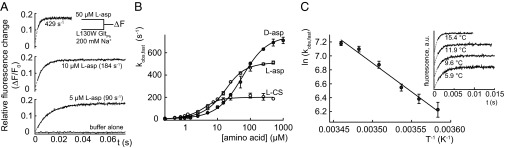
Concentration and temperature dependence of amino acid binding rates to L130W GltPh. (A) The tryptophan fluorescence transients after the rapid mixing of L130W GltPh in 200 mM NaCl with various [l-aspartate]. Gray traces represent fits of the sum of two exponential functions to the experimental data (black), which were performed with rates and amplitudes of the slower component fixed to a value that was previously assessed from a longer recording. The parameters were (relative amplitudes in parentheses) 429 s−1 (0.17) and 0.5 s−1 (0.018) for 50 µM l-aspartate, 184 s−1 (0.18) and 0.5 s−1 (0.017) for 10 µM l-aspartate, and 89 s−1 (0.17) and 0.5 s−1 (0.017) for 10 µM l-aspartate. The data during the dead time of the apparatus (2.3 ms) are represented as a broken line. For each trace, the fitted value for kobs,fast is presented. (B) The [amino acid] dependence of kobs,fast. The continuous lines represent the fits of Eq. 1 to the data. (C) An Arrhenius plot of kobs,fast because of the addition of 100 µM l-aspartate in 500 mM NaCl according to the linearization of the Arrhenius equation, 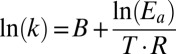 , where B represents the frequency factor, Ea represents the Arrhenius activation energy, T represents the absolute temperature, and R represents the universal gas constant. The continuous line represents the fit of a linear function to the data, which results in Ea = 68 ± 6 kJ mol−1. (Inset) Fluorescence transients at different temperatures that were used to generate the Arrhenius plot. All error bars represent ±SEM of at least three experiments.
, where B represents the frequency factor, Ea represents the Arrhenius activation energy, T represents the absolute temperature, and R represents the universal gas constant. The continuous line represents the fit of a linear function to the data, which results in Ea = 68 ± 6 kJ mol−1. (Inset) Fluorescence transients at different temperatures that were used to generate the Arrhenius plot. All error bars represent ±SEM of at least three experiments.
