Table 2.
Comparison of four methods in the simulation study
| Criteria | HSSVD | HSSVD-O | FITSSVD-O | LSHM-O | ||||
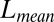 |
0.013 | (0.01) | 0.013 | (0.01) | 0.081 | (0.01) | 0.019 | (0.01) |
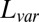 |
0.157 | (0.03) | 0.156 | (0.03) | NA | NA | ||
| Sparsity | 0.950 | (0.04) | 0.950 | (0.03) | 0.988 | (0.02) | 0.997 | (0.01) |
| BLK1 (mean) | 0.861 | (0.10) | 0.862 | (0.10) | 0.818 | (0.08) | 0.872 | (0.08) |
| BLK2 (mean) | 0.934 | (0.18) | 0.936 | (0.17) | 0.939 | (0.18) | 0.976 | (0.01) |
| BLK3 (mean) | 0.972 | (0.10) | 0.974 | (0.10) | 0.971 | (0.11) | 0.987 | (0.01) |
| BLK5 (mean) | 0.977 | (0.11) | 0.948 | (0.11) | 0.977 | (0.11) | 0.996 | (0.01) |
| BLK3 (var) | 0.977 | (0.02) | 0.977 | (0.02) | NA | NA | ||
| BLK4 (var) | 0.628 | (0.25) | 0.633 | (0.24) | NA | NA | ||
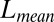 and
and 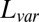 measure the difference between the approximated signal and the true signal, and so smaller is better. For the other measures of accuracy of bicluster detection, the larger the better. The rows BLK1 to BLK5 represent the biclustering detection rate for each bicluster.“-O” indicates that the oracle rank is provided.
measure the difference between the approximated signal and the true signal, and so smaller is better. For the other measures of accuracy of bicluster detection, the larger the better. The rows BLK1 to BLK5 represent the biclustering detection rate for each bicluster.“-O” indicates that the oracle rank is provided.
