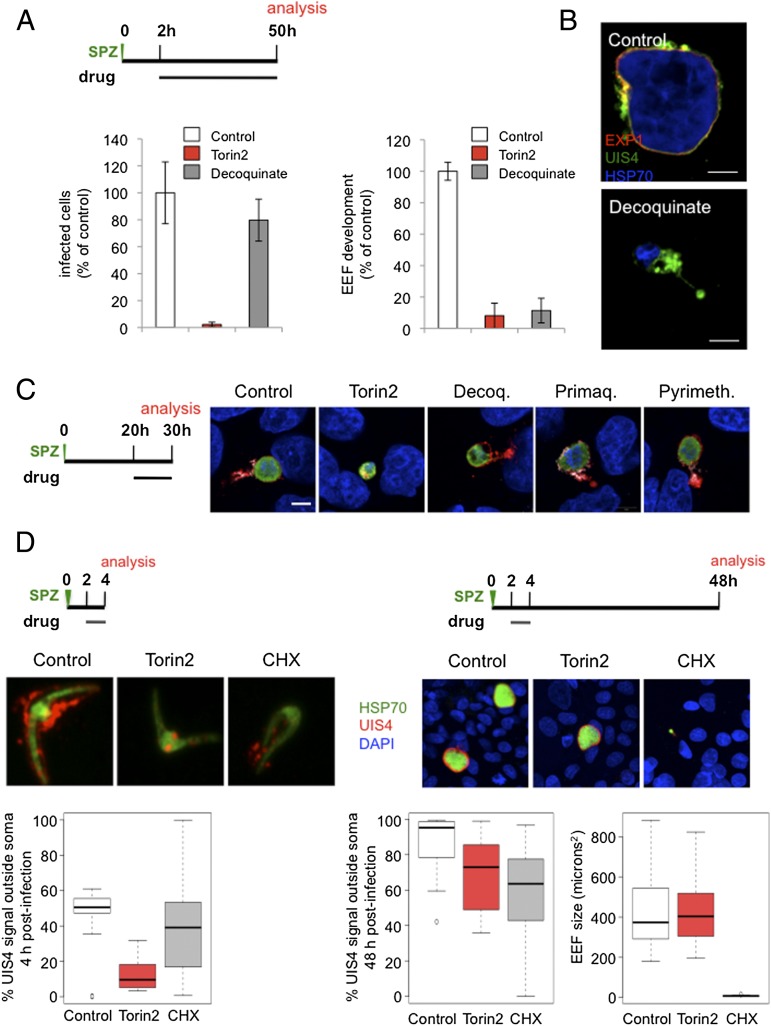
Fig. 6.
EEF elimination and PVM-resident protein-trafficking defects are torin-specific phenotypes, not general aspects of liver stage inhibition by antimalarials. (A and B) Effects of decoquinate and Torin2 on EEF numbers and development. (A) Schematic of treatment and analysis. Infected HepG2 cells analyzed by flow cytometry at 50 h after sporozoite addition. Mean of n = 3 biological experiments, each condition in triplicate. (B) Mouse primary hepatocytes infected ex vivo with EXP1 (red), UIS4 (green), and HSP70 (blue) labeling. (C) Effect of current antimalarial classes active against the liver stage at the onset of schizogony. Schematic illustrates experimental setup; representative confocal images shown with UIS4 (red), EXP1 (white), PbHSP70 (green), and DAPI (blue) labeling. (D) Effects of 2 h Torin2 or cycloheximide treatment on UIS4 localization and EEF development. Schematic illustrates experimental setup. Representative confocal images of control (DMSO), Torin2-, and cycloheximide-treated EEFs labeled with anti-UIS4 (red), anti-PbHSP70 (green), and DAPI (blue) 4 and 48 h postinfection. Quantification of the proportion of UIS4+ pixels not overlapping PbHSP70 in 20 EEFs from each condition at 4 and 48 h postinfection; quantification of EEF area 48 h postinfection.