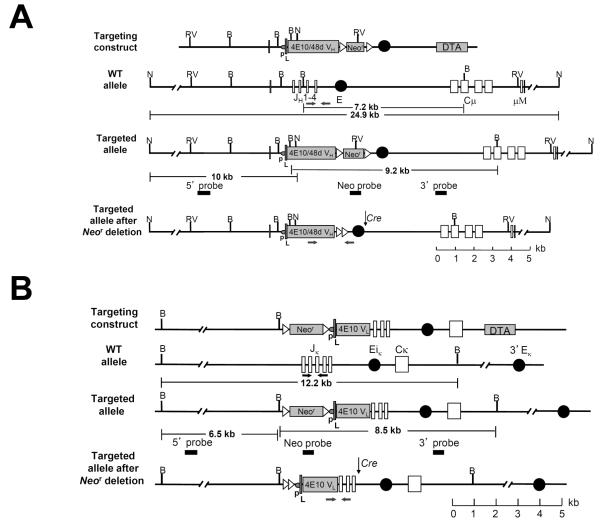
Figure 1. Targeted replacement of the mouse Igh and Igκ loci with the 4E10/48d VH(DH)JH and 4E10 VκJκ rearrangements, respectively.
(A-B) Site-directed strategies used to knock-in VH and VL regions, respectively, showing the Ig targeting constructs, targeted Ig alleles (shown before and after homologous recombination) and the targeted alleles after Cre-mediated neo cassette deletion. Restriction fragment sizes are indicated for both wild-type and targeted loci. B=BamHI. N=NdeI. RV=EcoRV. Genotyping primers are denoted by arrows. A. Genomic structure of the targeted Igh allele, showing the endogenous mouse JH cluster and Cμ region, as well as the 4E10/48d VH expression cassette, comprised of a J558 H10 family promoter (p), the H10 split leader sequence (L), and the rearranged 4E10/48d VH(DH)JH (4E10/48dVH) coding segment. B. Genomic structure of the targeted endogenous mouse Jκ cluster and Cκ region, as well as the 4E10 VL expression cassette, comprised of a VκOx1 promoter (p), the VκOx1 split leader sequence (L), and the rearranged 4E10 VκJκ (4E10VL) coding segment.