Abstract
The absence of normal high density lipoproteins (HDL) in Tangier disease is well established, but the properties of very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) and low density lipoproteins (LDL) in this disorder have not been well defined. The profiles obtained by analytic ultracentrifugation and the chemical composition, morphology, and electrophoretic mobility of Tangier and normal VLDL and LDL were compared. Apolipoproteins were fractionated by gel chromatography and characterized by amino acid analysis, polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, and immunochemical reactivity.
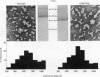
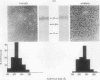
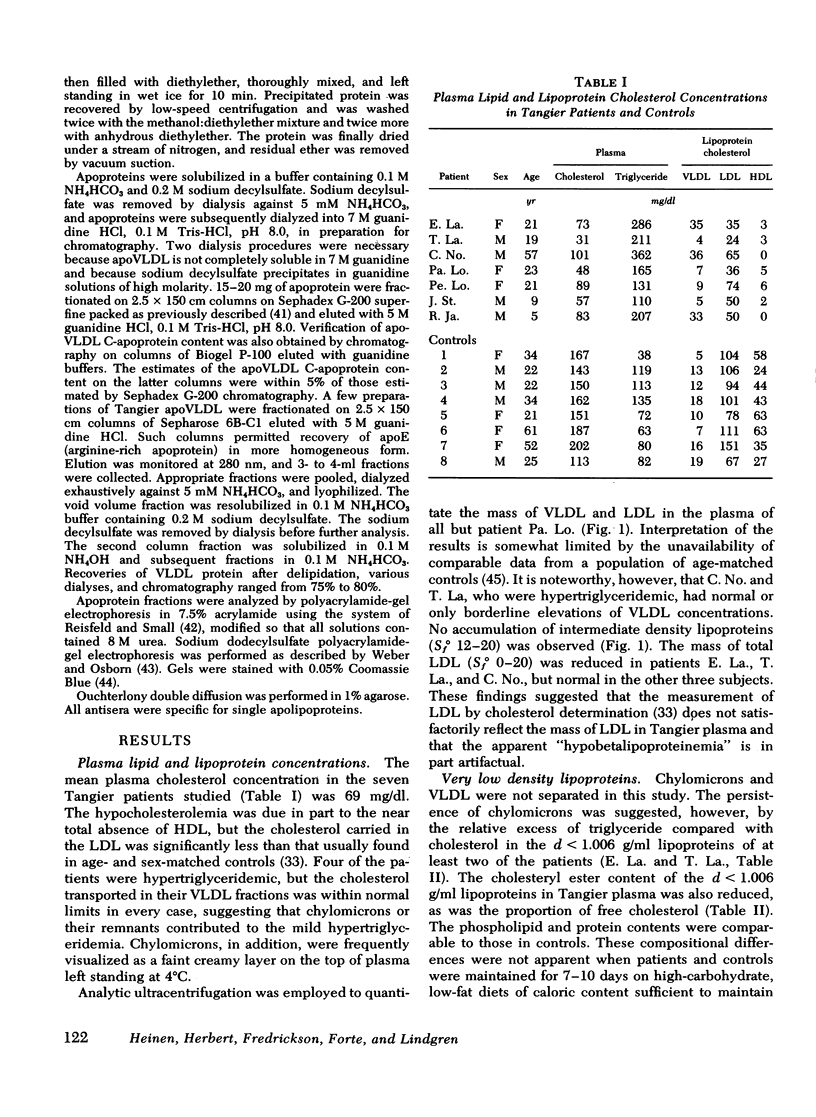
Concentrations of low density lipoproteins of Sfo 0-12 were reduced in three of six Tangier plasmas studied by analytic ultracentrifugation. Accumulation of intermediate density lipoproteins (Sfo 12-20) was not observed. Two subjects with hypertriglyceridemia had normal VLDL (Sfo 20-400) levels, suggesting that abnormalities of chylomicron metabolism probably account for the hypertriglyceridemia frequently observed in this disorder.
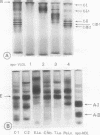
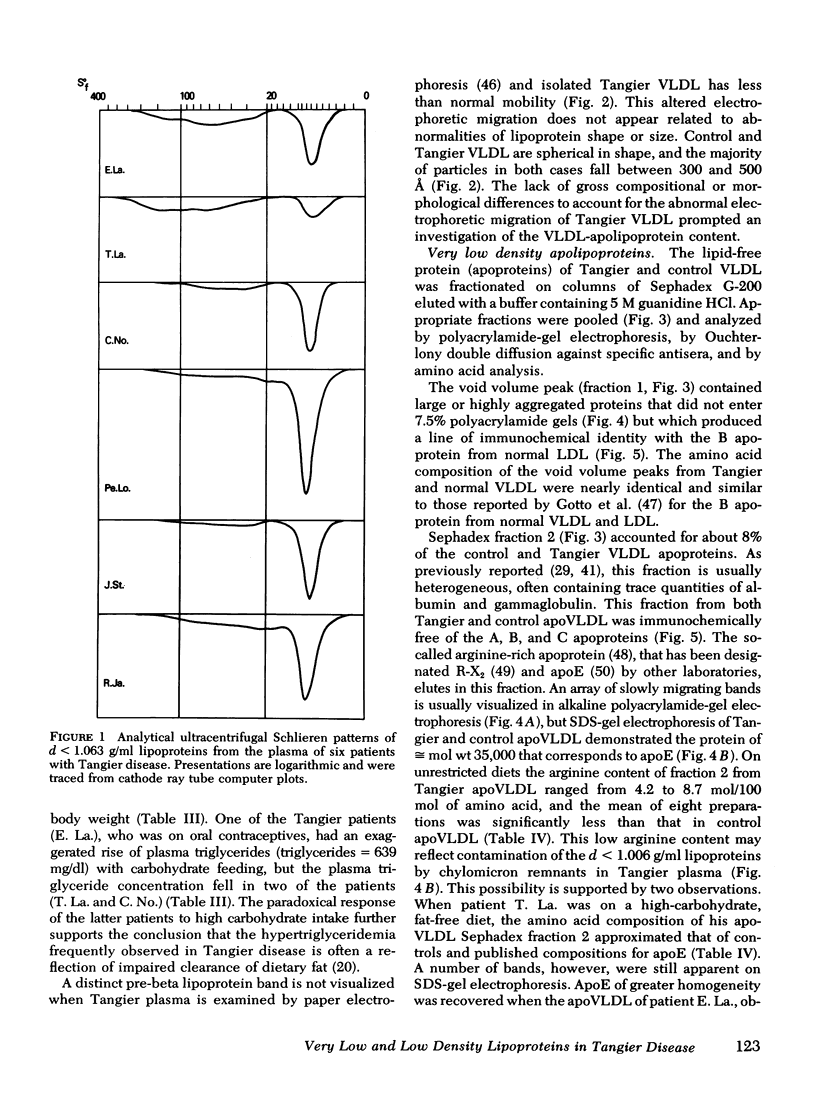
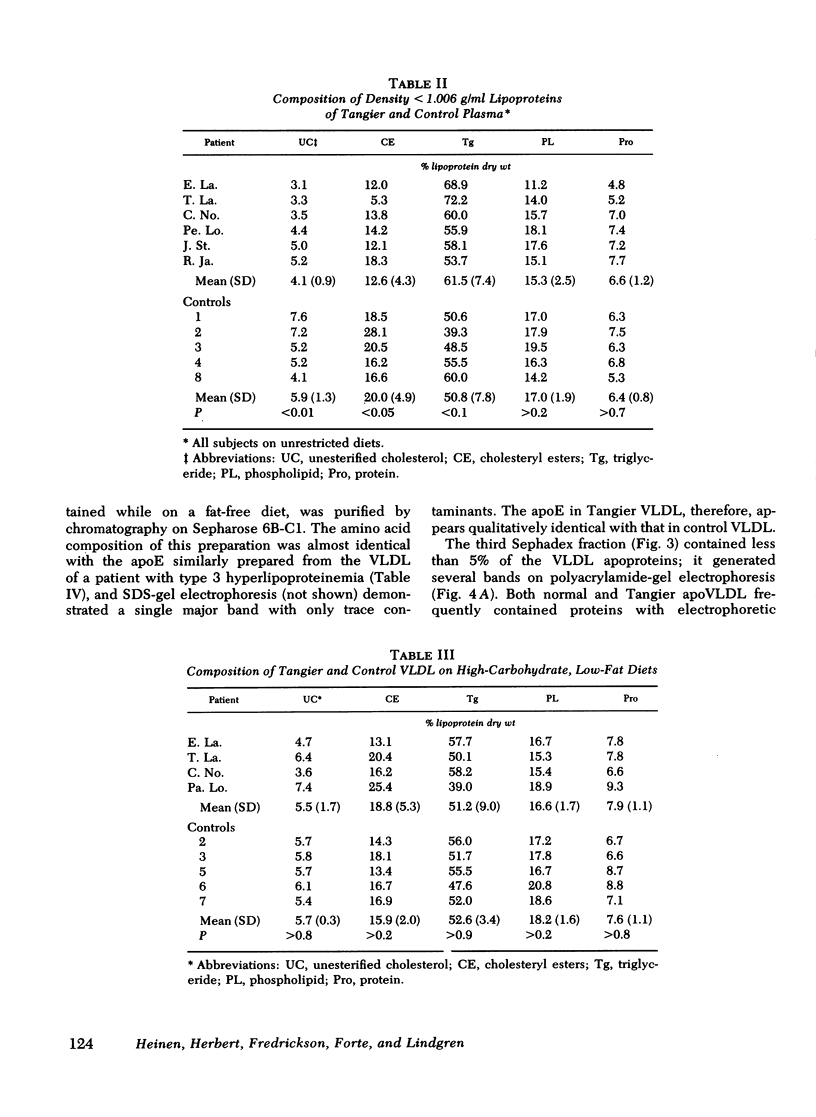
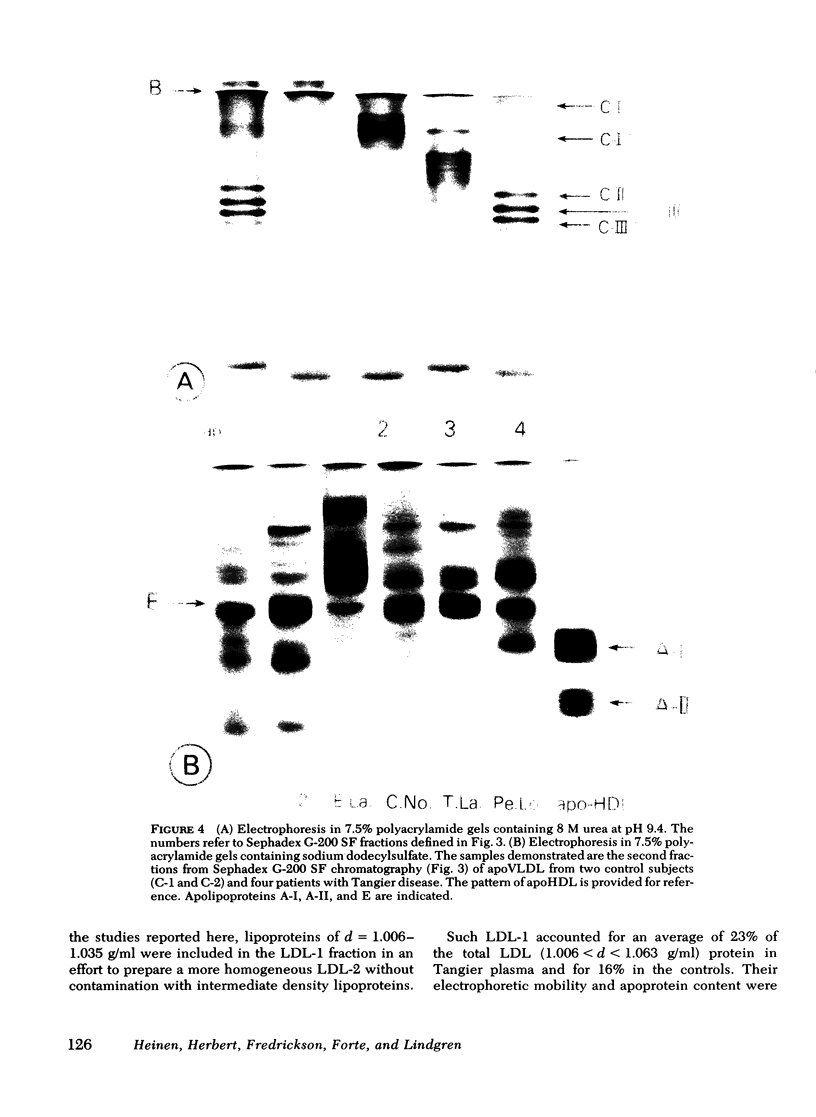
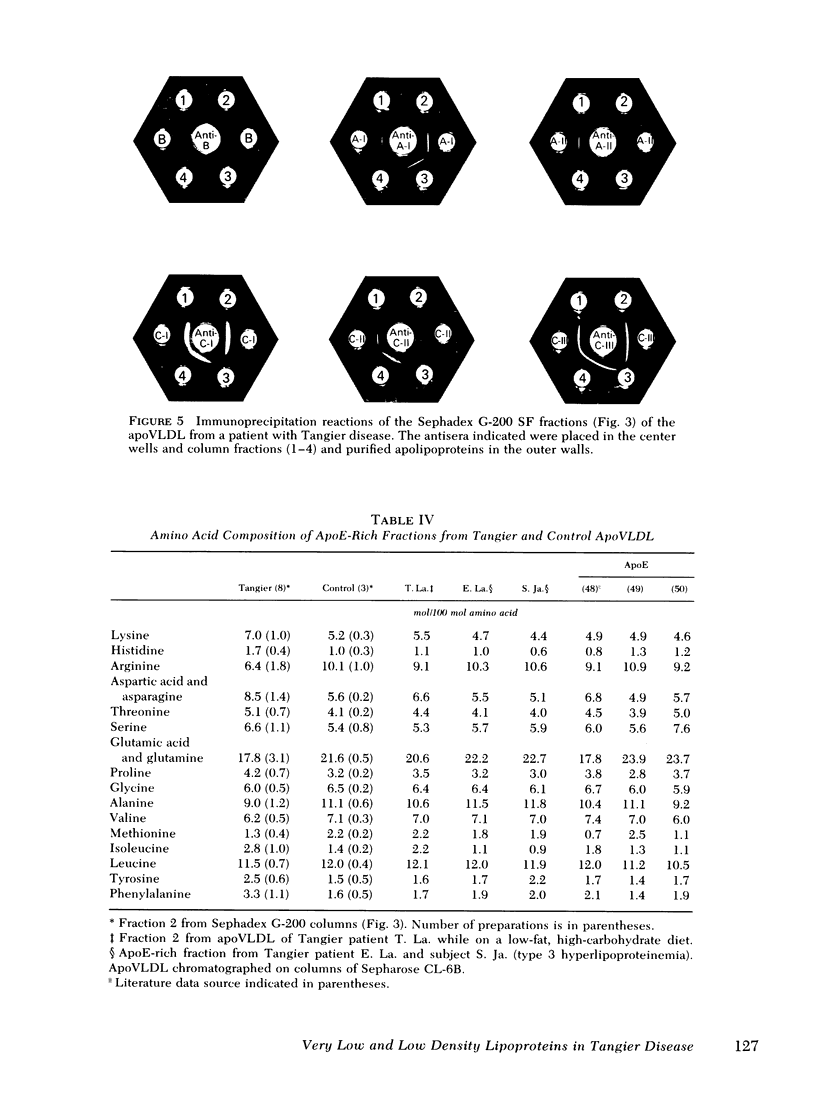
Tangier VLDL migrate more slowly than normal VLDL on paper electrophoresis, yet their morphology, gross chemical composition, and qualitative apolipoprotein content are similar. Quantitative abnormalities in C-apolipoproteins, however, were observed in Tangier VLDL. When patients were consuming unrestricted diets, C apoproteins accounted for 19-49% of the protein in lipoproteins of d < 1.006 g/ml. Ingestion of low-fat, high-carbohydrate diets reduced the VLDL-C-apoprotein content in all Tangier patients (mean = 17% of VLDL protein vs. 43% in controls). These findings suggested that a major proportion of the C apoproteins in Tangier plasma is associated with chylomicrons or their remnants, perhaps because the C-apoprotein reservoir normally provided by HDL is absent. This secondary mechanism for C-apoprotein conservation is lost when dietary fat is withdrawn.
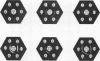
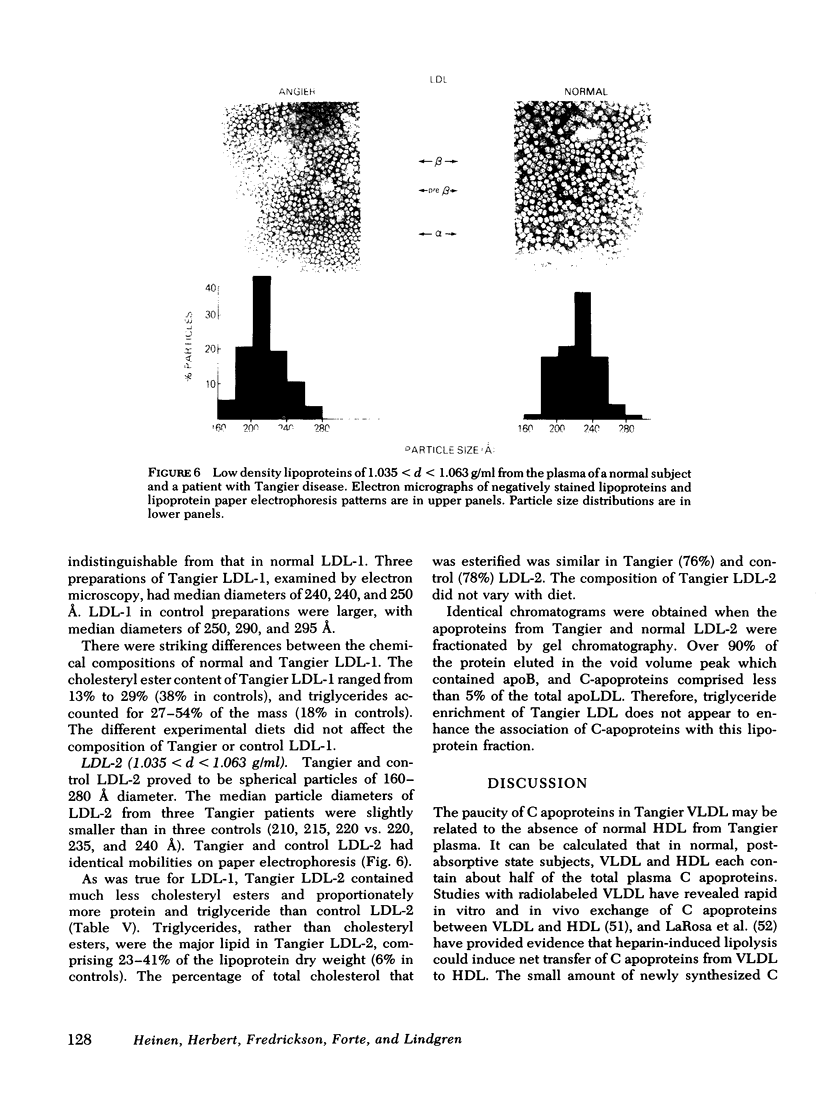
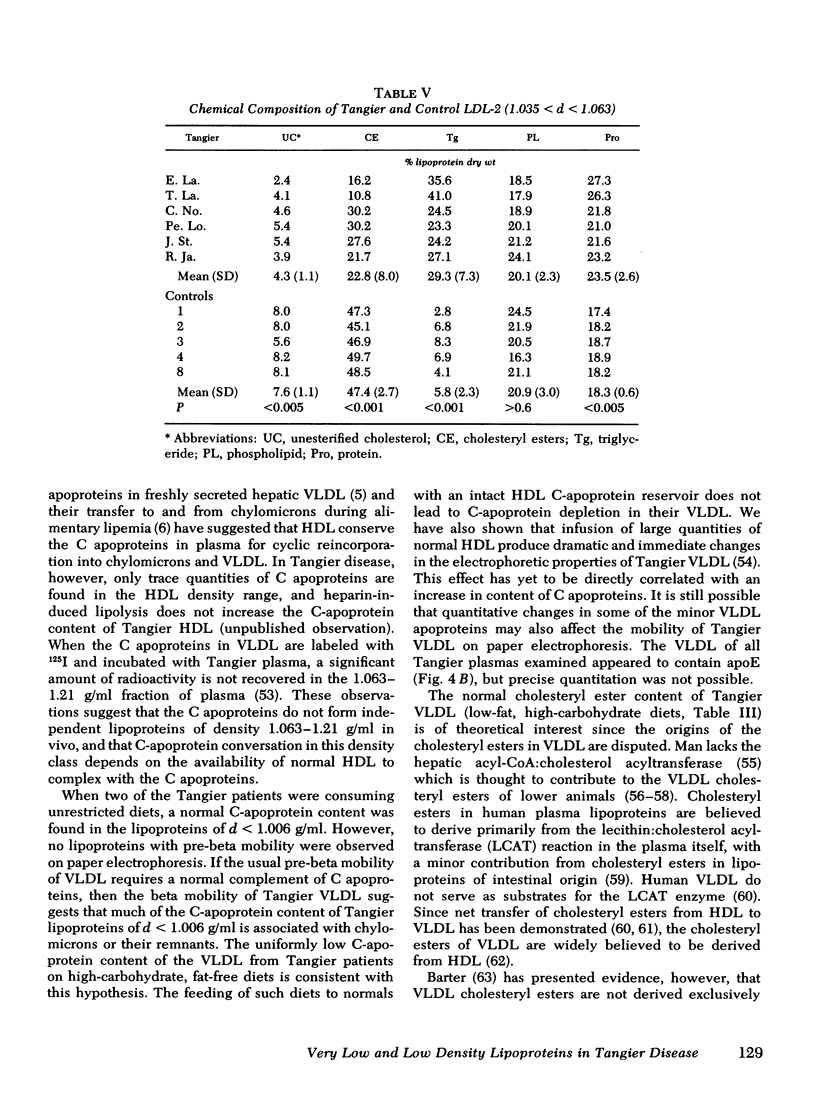
LDL-2 (1.035 < d < 1.063) from Tangier and control plasma had identical electrophoretic mobilities. Tangier LDL-2 had slightly smaller median diameters (210-225 Å vs. 230-240 Å in controls) and a quite different composition than normal LDL-2. Triglyceride accounted for a mean of 29% of Tangier LDL-2 mass (control = 6%) and the cholesteryl ester content was reduced by about 50%. Thus, HDL may be required for the generation of chemically normal LDL. Alternatively, the fundamental defect in Tangier disease may involve all lipoprotein classes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akanuma Y., Glomset J. In vitro incorporation of cholesterol-14C into very low density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S., Forte T. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal high density lipoprotein in Tangier Diesase. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):242–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barter P. J. Origin of esterified cholesterol transported in the very low density lipoproteins of human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jan;15(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier D. M., Havel R. J. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by lipoprotein fractions of human serum. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Baginsky M. L. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalvardjian A., Rudnicki E. Determination of lipid phosphorus in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jul;36(1):225–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T. On the metabolic conversion of human plasma very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):361–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Schurr D. Phospholipid removal during degradation of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1976 Nov;17(6):578–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K., Dorman J. D., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Neuropathy in Tangier disease. Alpha-Lipoprotein deficiency manifesting as familial recurrent neuropathy and intestinal lipid storage. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jul;17(1):1–9. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470250005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S. THE INHERITANCE OF HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN DEFICIENCY (TANGIER DISEASE). J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI104907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Fredrickson D. S. The pathology of Tangier disease. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):101–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Purification and substrate specificity of lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase from human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jul 8;15(5):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: structure of low and high density lipoproteins as revealed by elctron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI106586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 12;276(2):94–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701122760206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T. A comparison of heritable abnormal lipoprotein patterns as defined by two different techniques. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;47(11):2446–2457. doi: 10.1172/JCI105927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., CORNWELL D. G., NAKASATO D., ONCLEY J. L., HUGHES W. L., Jr, JANEWAY C. A. Studies on the metabolism of plasma proteins in the nephrotic syndrome. II. The lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):172–184. doi: 10.1172/JCI103596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidez L. I., Roheim P. S., Eder H. A. Turnover of cholesteryl esters of plasma lipoproteins in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jan;8(1):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Kirsch K. The apoproteins of various size classes of human chylous fluid lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 5;371(1):255–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Janssen E. T., Kennedy R., Dobbins J. Role of plasma lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase in the metabolism of high density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1966 Sep;7(5):638–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R., King W. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: lipid composition and reactivity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1827–1837. doi: 10.1172/JCI106400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. Physiological role of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Aug;23(8):1129–1136. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.8.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Birnbaumer M. E., Fredrickson D. S. Evidence for the identity of the major apoprotein in low density and very low density lipoproteins in normal subjects and patients with familial hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1486–1494. doi: 10.1172/JCI106945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greten H., Hannemann T., Gusek W., Vivell O. Lipoproteins and lipolytic plasma enzymes in a case of tangier disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 12;291(11):548–552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409122911103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Shore V. G., Shore B., Bier D. M. Role of specific glycopeptides of human serum lipoproteins in the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(4):595–600. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Forte T. M., Shulman R. S., La Piana M. J., Gong E. L., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S., Nichols A. V. Structural and compositional changes attending the ultracentrifugation of very low density lipoproteins. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):93–129. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Shulman R. S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Fractionation of the C-apoproteins from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4941–4946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman H. N., Fredrickson D. S. Tangier disease (familial high density lipoprotein deficiency). Clinical and genetic features in two adults. Am J Med. 1965 Oct;39(4):582–593. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. W. Studies in accelerated amino acid analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Potts J. T., Jr Improved recovery of methionine after acid hydrolysis using mercaptoethanol. Anal Biochem. 1969 May;29(2):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocen R. S., Lloyd J. K., Lascelles P. T., Fosbrooke A. S., Willims D. Familial alpha-lipoprotein deficiency (Tangier disease) with neurological abnormalities. Lancet. 1967 Jun 24;1(7504):1341–1345. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G., Holasek A. Characterization and quantitation of the apolipoproteins from human chyle chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1217–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further observations on the activation and inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoproteins. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):403–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Brown W. V., Fredrickson D. S. Changes in high-density lipoprotein protein composition after heparin-induced lipolysis. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):785–791. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Herbert P., Lux S. E., Fredrickson D. S. A specific apoprotein activator for lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren F. T., Adamson G. L., Jenson L. C., Wood P. D. Lipid and lipoprotein measurements in a normal adult American population. Lipids. 1975 Dec;10(12):750–756. doi: 10.1007/BF02532316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS A. V., SMITH L. EFFECT OF VERY LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS ON LIPID TRANSFER IN INCUBATED SERUM. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS A. V., SMITH L. EFFECT OF VERY LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS ON LIPID TRANSFER IN INCUBATED SERUM. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Bloch K. J., Isselbacher K. J. Very-low-density lipoprotein in intestinal lymph: evidence for presence of the A protein. Science. 1968 Dec 13;162(3859):1285–1286. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Frank A., Shames D. M., Berman M., Steinberg D. Very low density lipoprotein triglyceride transport in type IV hyperlipoproteinemia and the effects of carbohydrate-rich diets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2281–2297. doi: 10.1172/JCI106448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Small P. A., Jr Electrophoretic heterogeneity of polypeptide chains of specific antibodies. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose H. G. Origin of cholesteryl esters in the blood of cholesterolfed rabbits: relative contributions of serum lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase and hepatic ester synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):312–326. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelburne F. A., Quarfordt S. H. A new apoprotein of human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1428–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar A. K., Garner C. W., Baker H. N., Sparrow J. T., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Smith L. C. Effect of the human plasma apolipoproteins and phosphatidylcholine acyl donor on the activity of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3057–3064. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. J. Cholesteryl ester metabolism in liver and blood plasma of various animal species. Atherosclerosis. 1974 May-Jun;19(3):393–406. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(74)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T. The existence of an acid cholesterol esterase in human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 23;270(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Isolation and partial characterization of an arginine-rich apolipoprotein from human plasma very-low-density lipoproteins: apolipoprotein E. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jul;356(7):1113–1121. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.2.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Schoenborn W. Plasma lipoprotein abnormalities in a case of primary high-density lipoprotein (HDL) deficiency. Clin Genet. 1975 Oct;8(4):258–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I. Biosynthesis of lymph and plasma lipoprotein apoproteins by isolated perfused rat liver and intestine. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK B., DICKENMAN R. C., WHITE E. G., BURNETT H., CHERNEY P. J. Rapid estimation of free and total cholesterol. Am J Clin Pathol. 1954 Nov;24(11):1307–1315. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/24.11_ts.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]