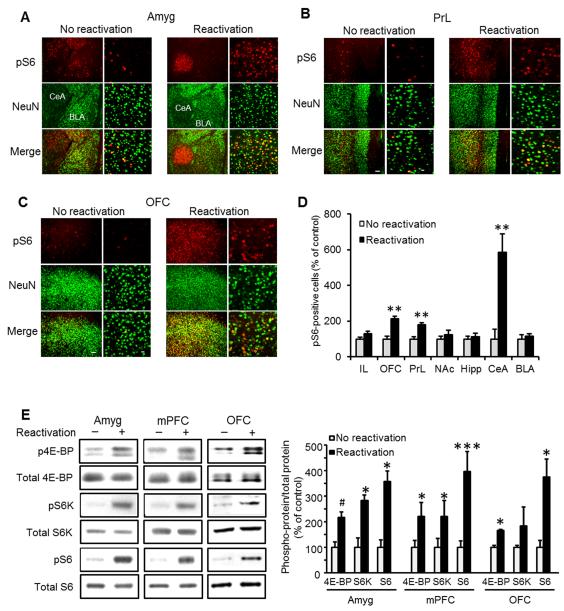
Figure 1. The mTORC1 signaling pathway is activated in the central amygdala, medial prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortices following reactivation of alcohol-associated memories.
A-C. Immunohistochemical staining of S6 phosphorylation 30 min after reactivation of alcohol-associated memory. Shown is dual-channel immunofluorescence images of phosphoS6 (pS6, red), NeuN (a marker for neurons, green), and overlay (yellow), in the basolateral (BLA) and central (CeA) nuclei of the amygdala (A), the prelimbic (PrL) region of the medial prefrontal cortex (B), and the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC; C). Images are representative of results from 4 rats (3-4 sections/region/rat). Scale bar, left: 100 μm; right: 20 μm. Quantification of the immunohistochemical staining of pS6-positive cells normalized by the total area in 3 slices per brain region from each rat. Data are mean ± SEM (t’s(6)>4.17; **p<0.01, n=4). D. Quantification of the immunohistochemical staining of S6 phosphorylation. Data are mean ± SEM expressed as percentage of no reactivation controls (t’s(6)>4.17; **p<0.01, n=4). IL=infralimbic cortex, OFC-orbitofrontal cortex, PrL=prelimbic cortex, NAc=nucleus accumbens, Hipp=dorsal hippocampus, CeA=central nucleus of the amygdala, BLA=basolateral amygdala E. Western blot analyses of 4E-BP, S6 kinase (S6K) and S6 phosphorylation in the amygdala (Amyg), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and OFC. Immunoreactivity of 4E-BP, S6K and S6 phosphorylation was normalized to the total protein and expressed as percentage of control (no reactivation). Data are mean ± SEM, (t’s(6)>2.50; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005, #p=0.08, n=4 per group).