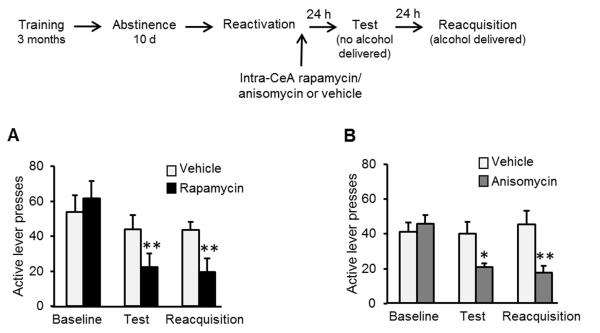
Figure 4. Infusion of rapamycin or anisomycin into the CeA after reactivation of alcohol-associated memories attenuates relapse.
A&B. Effects of rapamycin (A; 50 μg/side) or anisomycin (B; 62.5 μg/side) or vehicle infused into the CeA immediately after memory reactivation on lever presses during test and reacquisition. Data are mean ± SEM of active lever presses before abstinence (baseline), and during retention test and reacquisition stages. (A, rapamycin: Two-way ANOVA; Stage X Treatment interaction [F(2,14)=10.95, p<0.005]; post-hoc comparisons **p<0.01, n=8; B, anisomycin: Two-way ANOVA; Stage X Treatment interaction [F(2,11)=8.59, p<0.005]; post-hoc comparisons *p<0.5, **p<0.01, n=6-7).