Figure 8.
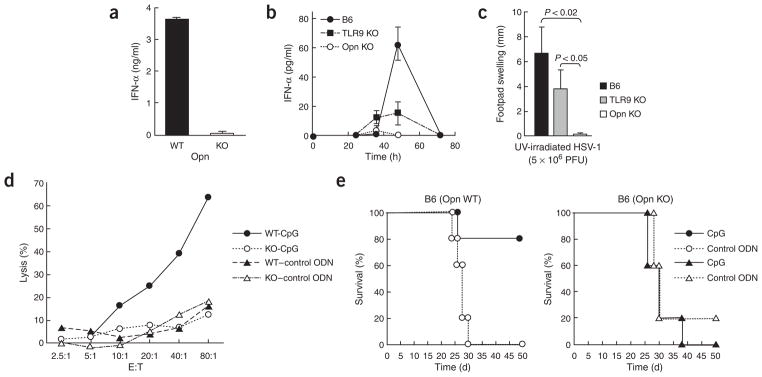
Opn-dependent in vivo response to HSV-1 infection. (a) IFN-α concentrations from Opn wild-type (WT) and Opn-deficient (KO) pDC culture supernatants after incubation in vitro with ultraviolet irradiation–treated (UV-irradiated) HSV-1 for 24 h. (b) Serum IFN-α in B6, B6 TLR9-deficient (TLR9 KO) and B6 Opn-deficient (Opn KO) mice injected intraperitoneally with HSV-1 (1 × 106 PFU/mouse). Data represent three mice per group. (c) HSV-1-specific delayed-type hypersensitivity responses in B6, TLR9 KO and Opn KO mice injected intraperitoneally with HSV-1 (5 × 106 PFU/mouse) and challenged 6 d later in the left footpad with ultraviolet irradiation–treated HSV-1 (1 × 105 PFU/mouse). Error bars indicate mean ± s.d. of three mice per group. (d) 51Cr-release assay of NK cells from B6 Opn wild-type (WT) and Opn-deficient (KO) mice, evaluated against YAC-1 cells. Draining lymph nodes of mice injected with CpG (ODN-1585; -CpG) or control GpC (–control ODN) were pooled. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (e) Survival of Opn WT and Opn KO mice injected intraperitoneally with 5 × 103 B16 cells plus 100 μg CpG (ODN-1585) or control GpC (control ODN). There were five mice in each group.
