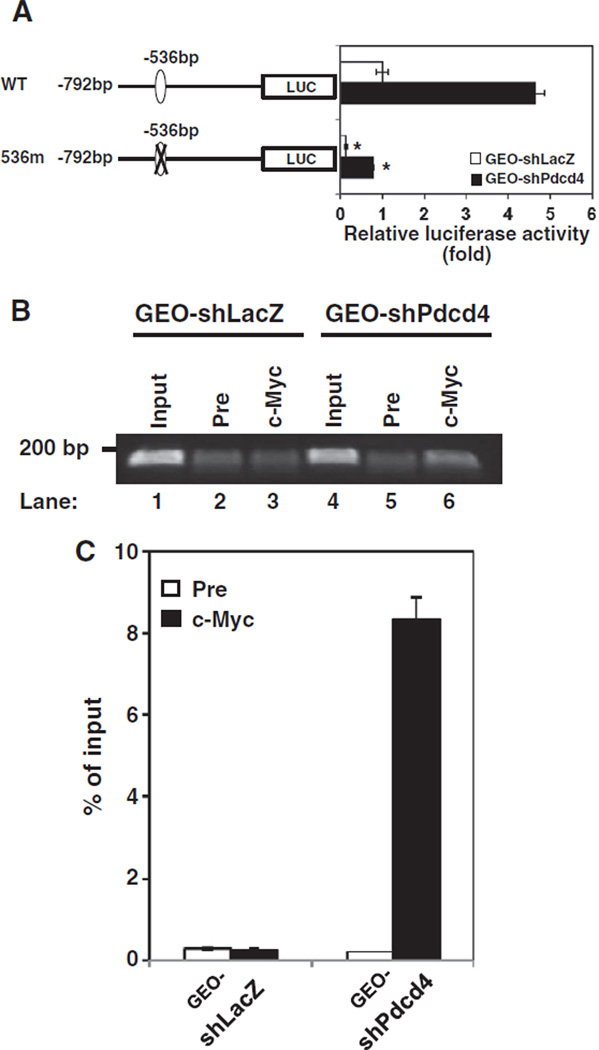
Fig. 3.
The c-Myc binding site at−536 of the map4k1 promoter responds to c-Myc regulation. (A) Pdcd4 knockdown stimulates map4k1 promoter activity. The pMAP4Kl(792)-LUC (WT) or 536m promoter construct (0.2 µg) was transfected into GEO-shLacZ and GEO-shPdcd4 cells along with 10 ng of pRL-SV40. The activity of GEO-shLacZ cells transfected with WT is designated as 1. Three independent experiments were performed with 5 replicates for each sample. The represented data are shown and expressed as mean±SD (n=5). The asterisk denotes a significant difference compared with cells transfected with WT as determined by one-way ANOVA (P<0.0001). (B and C) c-Myc directly binds to the map4k1 promoter in Pdcd4 knock-down cells. ChIP assays were performed with cell lysates from either GEO-shLacZ or GEO-shPdcd4 cells using control preimmune IgG (Pre) or anti-c-Myc antibody (c-Myc). The DNAs from cell lysate (input) and ChIP enriched were quantified by qPCR using primers for amplifying the c-Myc binding site at −536 bp on the promoter of MAP4K1. The representative PCR products were resolved onto 2% agarose gels (B). The level of the target gene in immunoprecipitated DNA of each sample is compared to that in input chromatin, which is equivalent to 100% (C).