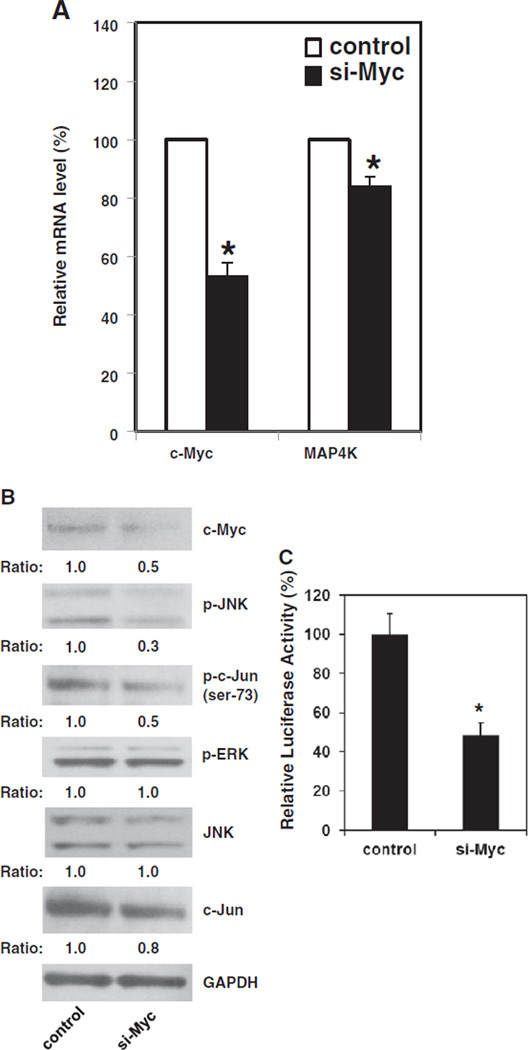
Fig. 4.
Down-regulation of c-Myc reverses MAP4K1 expression in Pdcd4 knock-down cells. The cells transfected with c-myc siRNA (si-Myc) or scramble siRNA (control) along with pMACS K+.II plasmid were collected for extracting RNA or making cell ly-sates. The c-Myc knockdown cells were enriched by H-2Kk antibody conjugated beads as described in Materials and methods. (A) The mRNA level of map4k1 decreased in c-Myc knock-down cells. The total RNAs from control and si-Myc cells were reverse transcribed and subjected to qPCR. The ratio of c-myc/GAPDH and map4k1/GAPDH in control cells is designated as 100%. Two independent experiments were performed with 3 replicates for each sample. The data are shown and expressed as mean ± SD. The asterisk indicates a significant difference compared with control cells as determined by one-way ANOVA (P<0.05). (B) c-Myc knockdown decreases the phosphorylation of JNK and c-Jun (ser-73). The cell lysates from control and si-Myc cells were subjected to Western blot analysis using various antibodies as indicated. The ratio of target protein/GAPDH in control cells is designated as 1.0. (C) Knockdown of c-Myc inhibits AP-1 dependent transcription. The relative luciferase activity in control cells is designated as 100%. Three independent experiments were performed with 5 replicates for each sample. The represented data are shown and expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5). The asterisk indicates a significant difference as determined by one-way ANOVA (p<0.005).