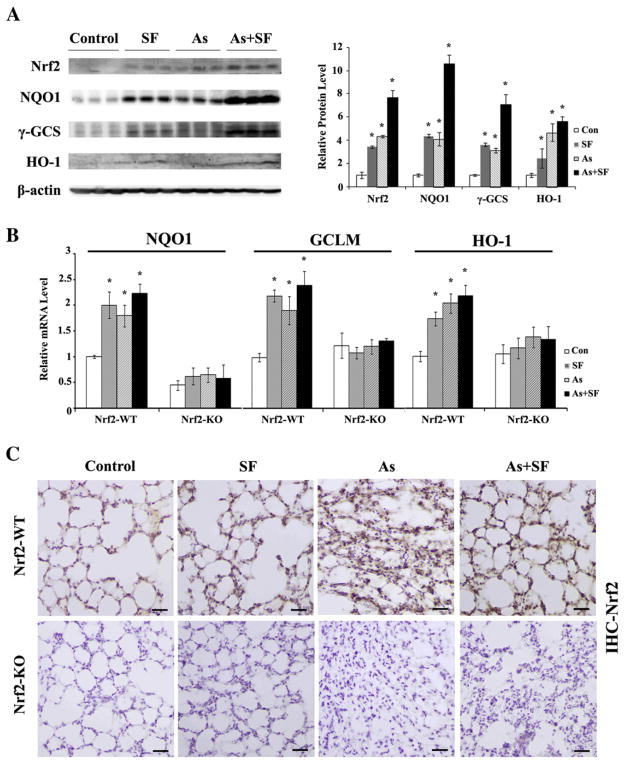
Fig. 1.
The lungs of mice exposed to arsenic particles and/or SF have elevated levels of Nrf2 and its target genes. (A) The lungs from Nrf2-WT mice were homogenized. Equal amounts of tissue lysate (200 μg total protein per lane) were loaded and subjected to immunoblot analysis. Each lane represents an individual mouse (right panel). The relative band intensity (to β-actin) was plotted (left panel) (B) mRNA levels of NQO1, GCLM, and HO-1 in Nrf2-WT and Nrf2-KO were analyzed by qRT-PCR. mRNA was extracted from three mice per group and used to run qRT-PCR in duplicate. Results are expressed as means±SD (n=3: SD was calculated from the mean of three mice), *p<0.05 versus respective “Con”. (C) IHC staining of lung tissue sections from both Nrf2-WT and Nrf2-KO in untreated (control), SF-injected (SF), arsenic-inhaled (As), and arsenic-inhaled plus SF-injected (As+SF) groups. Scale bar: 100 μm.