Fig. 2.
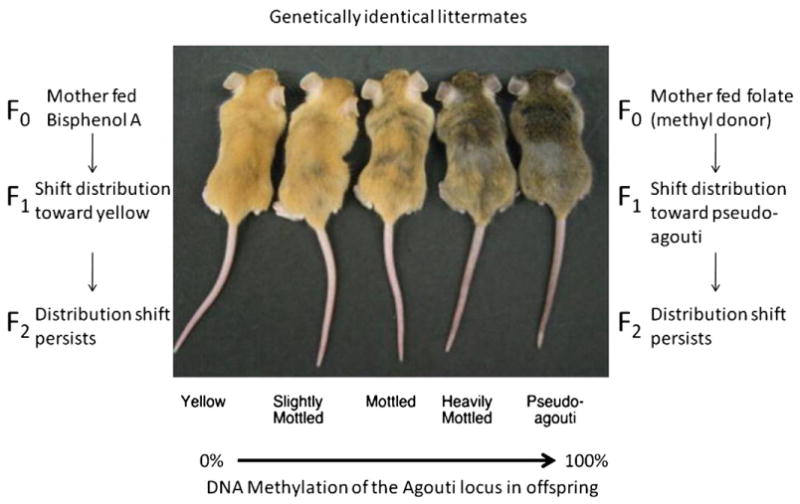
DNA methylation changes at the Agouti locus in the viable yellow agouti (Avy) mouse are phenotypically detectable and environmentally influenced. Littermates from the viable yellow agouti mouse strain are pictured. Coat color varies in these mice across a spectrum from yellow to agouti. The differences in coat color are due to a change in DNA methylation at the Agouti locus. The mice that harbor loci that exhibit a low level of Agouti methylation (for example, 0%) are yellow, while mice with a high level of DNA methylation (for example, 100%) appear agouti (brown). Treatment with BPA or folic acid can shift coat color distribution toward yellow or agouti, respectively. This coat color shift persists to the next generation indicating that the epigenetic change that occurs at the agouti locus is heritable (Morgan et al. 1999; Blewitt et al. 2006). Picture adapted from (Dolinoy et al. 2006).
