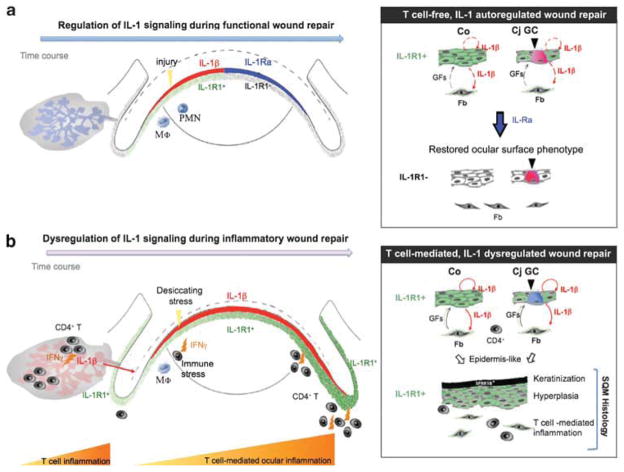
Figure 8.
Schematic model proposing an integral role for interleukin (IL)-1/IL-1 receptor type 1 (IL-1R1) signaling in the molecular events of CD4+ T-cell-mediated inflammation and dysregulated homeostatic tissue repair in ocular squamous metaplasia (SQM). (a) Epithelial IL-1/IL-1R1 signaling is an essential, cytokine-mediated mechanism for tissue repair. Upon wounding, pre-stored IL-1β (shown in red) is released by the ocular epithelium to rapidly recruit innate immune cells (eg, neutrophils (PMN), macrophages (Mφ)) to the injury site where they elicit transient local inflammation. IL-1β induces IL-1R1 expression on epithelial and stromal cells of the ocular surface. Through its interactions with IL-1R1-expressing stromal cells, IL-1β activates limbal and corneal fibroblasts (Fb) to secrete growth- and migration-promoting factors, such as keratinocyte and hepatocyte growth factors (GFs), respectively.43,44 In the later stages of re-epithelialization, regenerated ocular epithelial cells shut down the IL-1-mediated repair machinery by upregulating key inhibitory factors, such as IL-1Ra (shown in blue).45,46 The ocular mucosal phenotype is restored, consisting of a transparent, non-keratinized corneal (Co) epithelium and neutral mucin-secreting goblet cells (GCs) in the conjunctiva (Cj). (b) With chronic infiltration of IFNγ-producing autoreactive CD4+ effector T cells, IL-1’s counterbalancing system is disrupted, as evidenced by the ongoing production of IL-1β (shown in red), the persistent expression of IL-1R1 throughout the ocular surface (shown in green) and the decreased IL-1Ra/IL-1β ratio. Unopposed IL-1/IL-1R1 signaling promotes defective cell growth and differentiation, leading to the characteristic SQM phenotype with the upregulation of cornified envelope proteins (eg, small proline-rich protein 1B (SPRR1B)), epithelial hyperplasia, as well as the depletion and acidification of mucin-secreting GCs. Collectively, this model places the IL-1/IL-1R cytokine system in a central role during the development of autoimmune-mediated SQM.