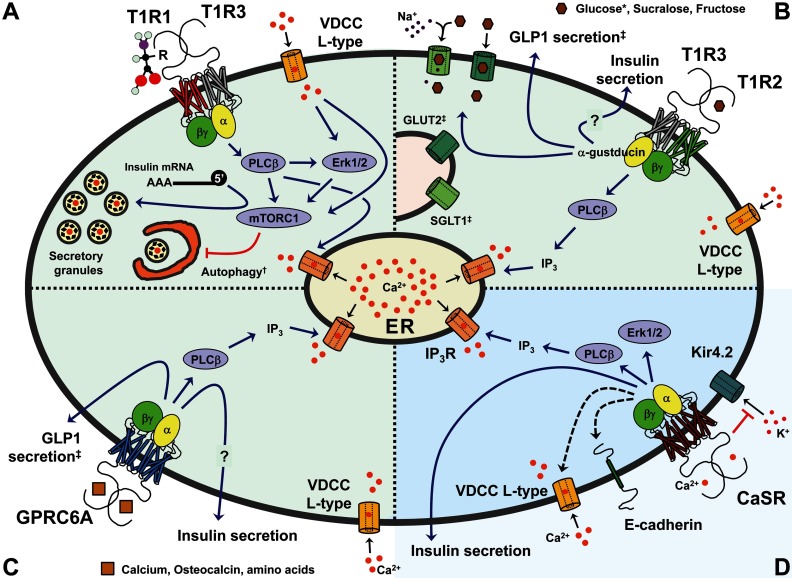
Figure 1.
Signaling through T1R1/T1R3, T1R2/T1R3, GPRC6A, and CaSR in β- or Gut Cells. In light green are GPCRs that can be directly activated by amino acids and use calcium as an allosteric regulator (A–C), whereas in blue is the CaSR whose main ligand is calcium and can be allosterically regulated by amino acids (D). See Table 1 for a comprehensive list of agonists, allosteric activators, and inhibitors for the reviewed GPCRs. A, T1R1/T1R3 receptor. In β, heart, and HeLa cells, the receptor activates PLCβ, ERK1/2, and mTORC1 and promotes release of calcium stores. Together, these pathways positively regulate 5′-cap-dependent transcription of the insulin message and may also promote insulin secretion. Receptor knockdown cells display reduced insulin levels and rampant autophagy. B, T1R2/T1R3 receptor. In enterocyte l-cells, the receptor activates PLCβ and promotes GLP-1 secretion and increased plasma membrane expression of the glucose transporters SGLT1 (sodium-dependent glucose co-transporter 1) and GLUT2 (glucose transporter 2). Signaling in β-cells is likely conserved and is proposed to regulate insulin secretion. C, GPRC6A receptor. In enterocyte l-cells the receptor activates PLCβ and promotes secretion of GLP-1. Signaling in β-cells is likely conserved and is proposed to regulate insulin secretion. D, CaSR receptor. In β-cells the receptor activates PLCβ and ERK1/2, induces release of ER calcium stores, stimulates expression of E-cadherin and l-type VDCC (black dotted arrows), inhibits Kir4.2 channels through protein-protein interactions, and promotes insulin secretion. The CaSR also regulates hormone secretion in other endocrine tissues. *, T1R2/T1R3 displays differential sensitivity for sweet compounds between humans and mice (4–6). †, Regulation of autophagy by the T1R1/T1R3 receptor was shown in heart and HeLa cells but not yet in β-cells. ‡, Described in enterocyte l-cells of the small intestine. See text and Table 1. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; IP3, inositol triphosphate; IP3R, IP3 receptor.