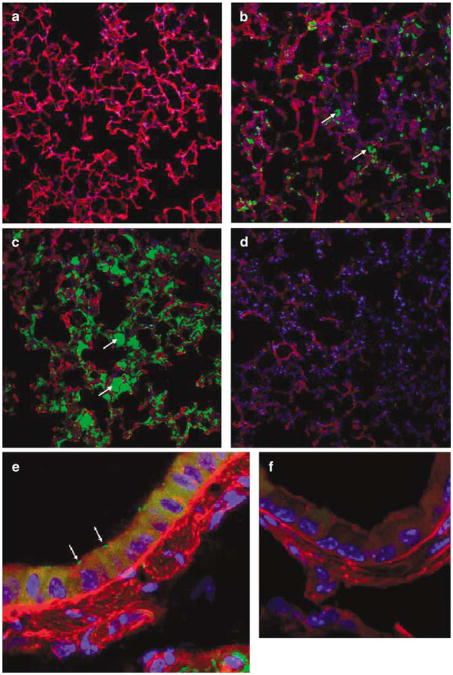
Figure 2.
Green fluorescent protein (GFP)-expressing invasive E. coli in the mouse lung. Lungs of mice were infected with invasive E. coli BM4570 carrying the prokaryotic expression plasmid pAT505 (GFP expressed under the control of the prokaryotic Plac promoter) with doses ranging from 5 × 107 to 5 × 109 CFU (colony-forming unit) per mouse. The lungs were harvested 1 h post-infection. Invasive E. coli were associated with the alveoli in a dose-related manner ((a) 5 × 107 CFU per mouse, (b) 5 × 108 CFU per mouse, (c) 5 × 109 CFU per mouse, (d) PBS (phosphate buffered saline) control). Original magnification × 20. Bacteria associated with airway epithelial cells were also detected ((e) mouse transfected with 5 × 109 CFU, (f) PBS control). Original magnification × 63. GFP-expressing bacteria appear in green, alveoli in red and 4-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained nuclei are shown in blue. Arrows indicate E. coli associated with alveoli and airway epithelial cells, respectively. Images are representative of 10 fields of views per section.