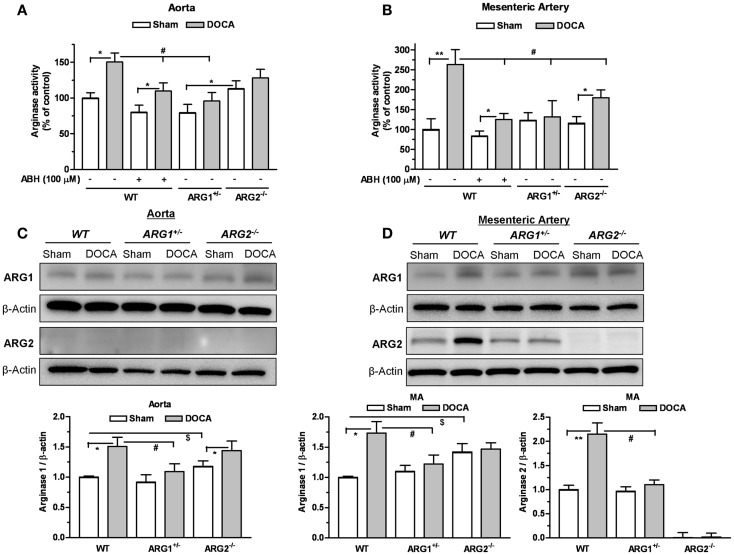
Figure 2.
Partial deletion of arginase 1 (ARG1+/−) or inhibition of arginase prevents DOCA-salt-induced increase in vascular arginase activity/expression. Arginase activity measured in aorta (A) and mesenteric artery (MA) (B) in WT uninephrectomized (WT Sham), WT uninephrectomized and DOCA-salt treated (WT DOCA), partial arginase 1 (ARG1+/−) knockout uninephrectomized (ARG1+/− Sham), ARG1+/− and DOCA-salt treated (ARG1+/− DOCA), arginase 2 (ARG2−/−) uninephrectomized (ARG2−/− KO Sham), and ARG2−/− KO DOCA-salt treated mice. Pretreatment with an inhibitor of arginase (ABH, 100 μM) prevented elevation of arginase activity in aorta and MA in WT-DOCA-salt treated mice (A,B). Measurement of protein expression of ARG1 and ARG2 in aorta (C) and MA (D) of animals treated with Sham or DOCA-salt treated WT, ARG1+/−, or ARG2−/− mice. Arginase activity in WT Sham group was considered as 100%. Data represents mean ± SEM of five to seven experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with its respective Sham group. #P < 0.05, compared with WT-DOCA group. $P < 0.05, compared with WT Sham group.