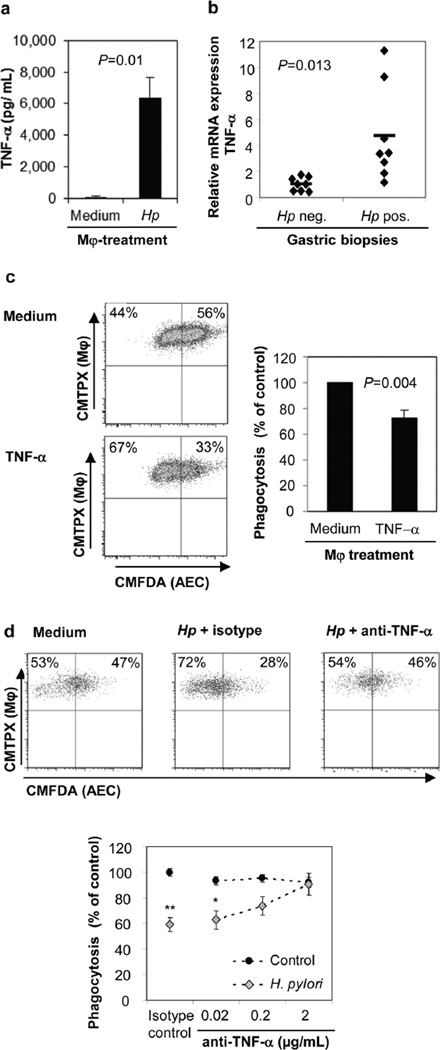
Figure 5. TNF-α mediates reduced apoptotic cell clearance by H. pylori treated macrophages.
(a) TNF-α concentrations in culture supernatants of macrophages treated with live H. pylori (MOI=10) or medium for 6 h were determined by ELISA, n=4. (b) Human H. pylori infection increases gastric expression of TNF-α. Gastric biopsies obtained from non-infected or H. pylori-infected human subjects were analyzed for TNF-α gene expression by quantitative real-time PCR, n=8. (c) Macrophage pre-treatment with rhTNF-α (10 ng/mL) inhibits phagocytosis of AECs. Representative FACS plots (left panels) and cumulative data from 4 experiments, mean ± SEM (right panel). (d) Neutralization of TNF-α in H. pylori-treated macrophage cultures reverses the suppressive effect of H. pylori on macrophage clearance of AECs. Macrophages were pre-treated for 6–8 h with both H. pylori and anti-TNF-α antibodies (or isotype control) prior to co-culture with Hp-AECs Representative FACS plots (top panels) and cumulative data from 3 experiments, mean ± SEM (bottom panel). *P≤0.05 and **P≤0.01 compared to untreated control; Student’s t test.