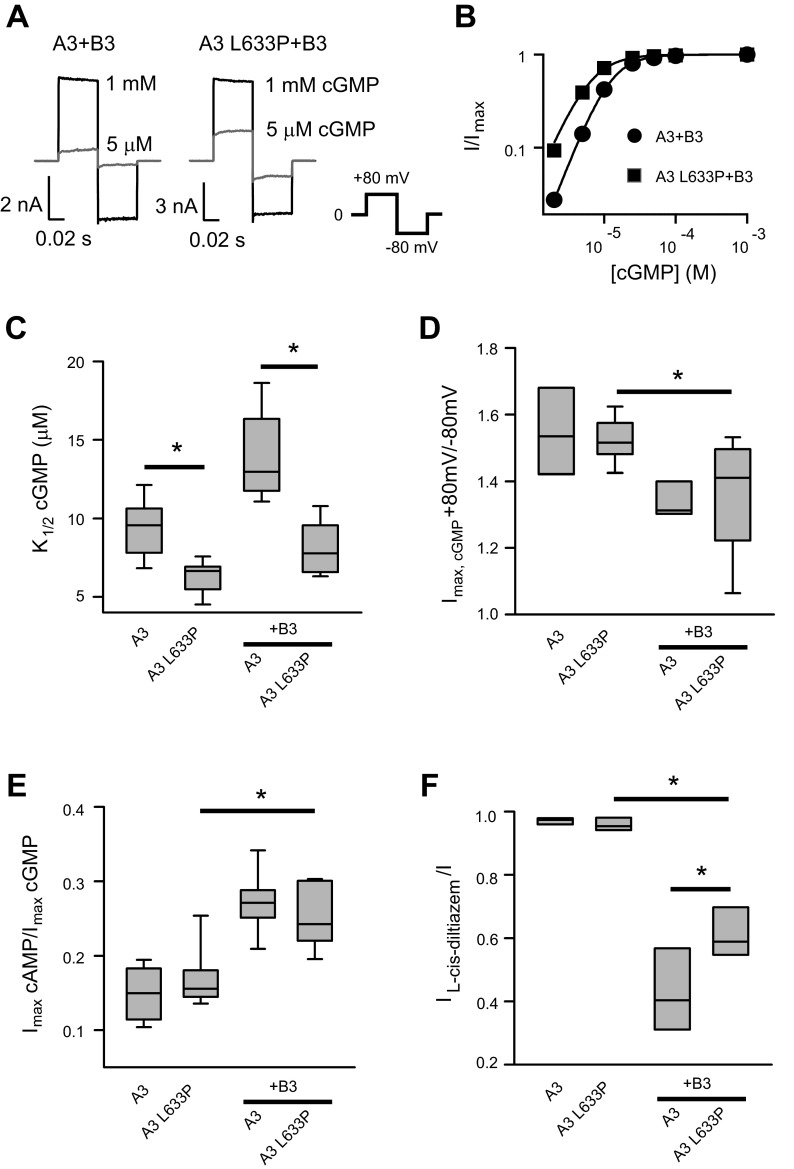
Fig. 1.
Summary of effects of L633P mutation on basic properties of homomeric and heteromeric cone cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels. A: representative currents elicited by saturating 1 mM cGMP (black) and 5 μM cGMP (gray) for heteromeric A3 + B3 channels composed of A3 wild-type or A3-L633P. Currents were elicited by voltage steps from a holding potential of 0 mV to + 80 mV, then to −80 mV and 0 mV. Leak currents in the absence of cyclic nucleotide were subtracted. B: representative cGMP dose-response relationships for activation of heteromeric A3 + B3 and A3 L633P + B3 channels, fitted with the Hill equation. C: K1/2,cGMP values for homomeric A3 channels and heteromeric A3 + B3 channels with or without the L633P mutation are shown using a box plot. The horizontal lines within the boxes indicate the median values; the bottom and top of the boxes show the 25th and 75th percentiles of the data, respectively; the ends of whiskers show the 5th and 95th percentiles of the data. D and E: outward current rectification (Imax,cGMP + 80 mV/−80 mV; D) and relative cAMP efficacy (Imax,cAMP/Imax,cGMP; E) of A3 and A3 + B3 channels were not significantly altered by L633P. F: l-cis-diltiazem inhibition of maximal cGMP current was attenuated by L633P. The ratio of cGMP current in the presence and absence of 25 μM l-cis-diltiazem (IL-cis-diltiazem/I) was 0.42 ± 0.05 (n = 8) for wild-type A3 + B3 channels and 0.62 ± 0.03 (n = 8) for A3-L633P + B3 channels. *P < 0.05.