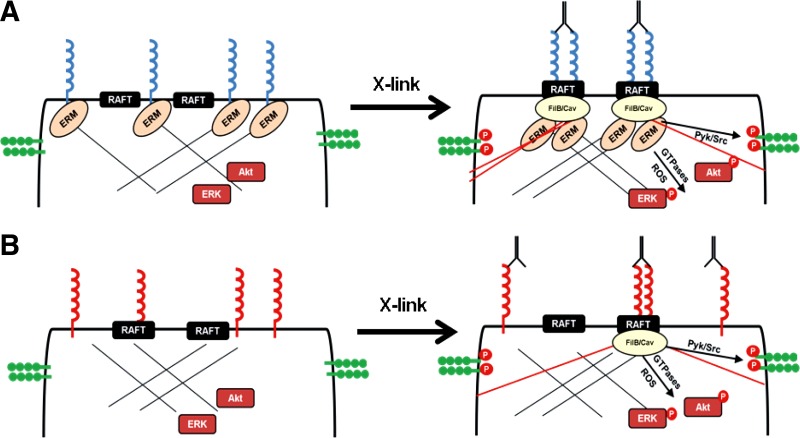
Fig. 7.
Proposed model for how distinct ICAM-1 glycoforms regulate adhesion and cell signaling. A: complex N-glycan containing ICAM-1 (fully matured) is expressed exclusively in nonraft domains and is bound to the actin cytoskeleton through interactions with the ERM complex. Upon cross-linking, ICAM-1 is transported into raft domains via these cystoskeletal interactions. Additionally, new interactions with filamin A/B and caveolin regulate new stress fiber formation leading to activation of cell signaling (VE-cadherin, Akt, and ERK). B: HM-ICAM-1 resides in both raft and nonraft regions of the plasma membrane during basal conditions and does not interact with the ERM complex. Upon cross-linking, new stress fiber formation is still achievable as some of the protein is already in the raft domains allowing for filamin A/B and caveolin interactions, albeit to a significantly lesser extent compared with complex ICAM-1.