Fig. 4.
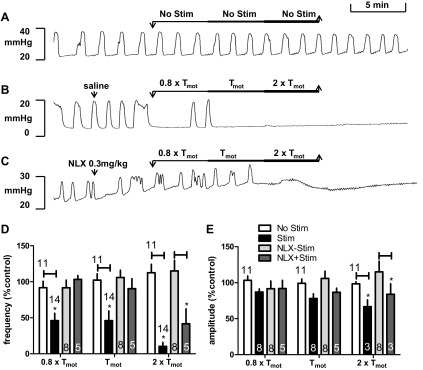
Intensity-dependent effects of spinal nerve stimulation on bladder contractions. A–C: typical experimental records showing the BRC. There was no significant change in BRC frequency or amplitude over the duration of the experiment if electrical stimulation was not applied (A, No Stim). Ten-Hertz spinal nerve stimulation (Stim) at 3 intensities relative to motor threshold (Tmot) for a total of 15 min stimulation (5-min duration of each intensity) attenuated bladder contractions (B). Following NLX injection, spinal nerve (SN) stimulation at 0.8 × Tmot and 1 × Tmot intensity produced mild reduction of bladder contractions and stimulation at 2 × Tmot abolished bladder contraction (C). D and E: summary of intensity- dependent effects of spinal nerve stimulation on frequency (D) and amplitude (E) of bladder rhythmic contraction without or with systemic administration of NLX (0.3 mg/kg). *P < 0.05, Student's t-test. Number of animals is indicated either above or in each bar. Responses are represented as a percentage of pretreatment values (%control), where the baseline response before stimulation is defined as 100%.
