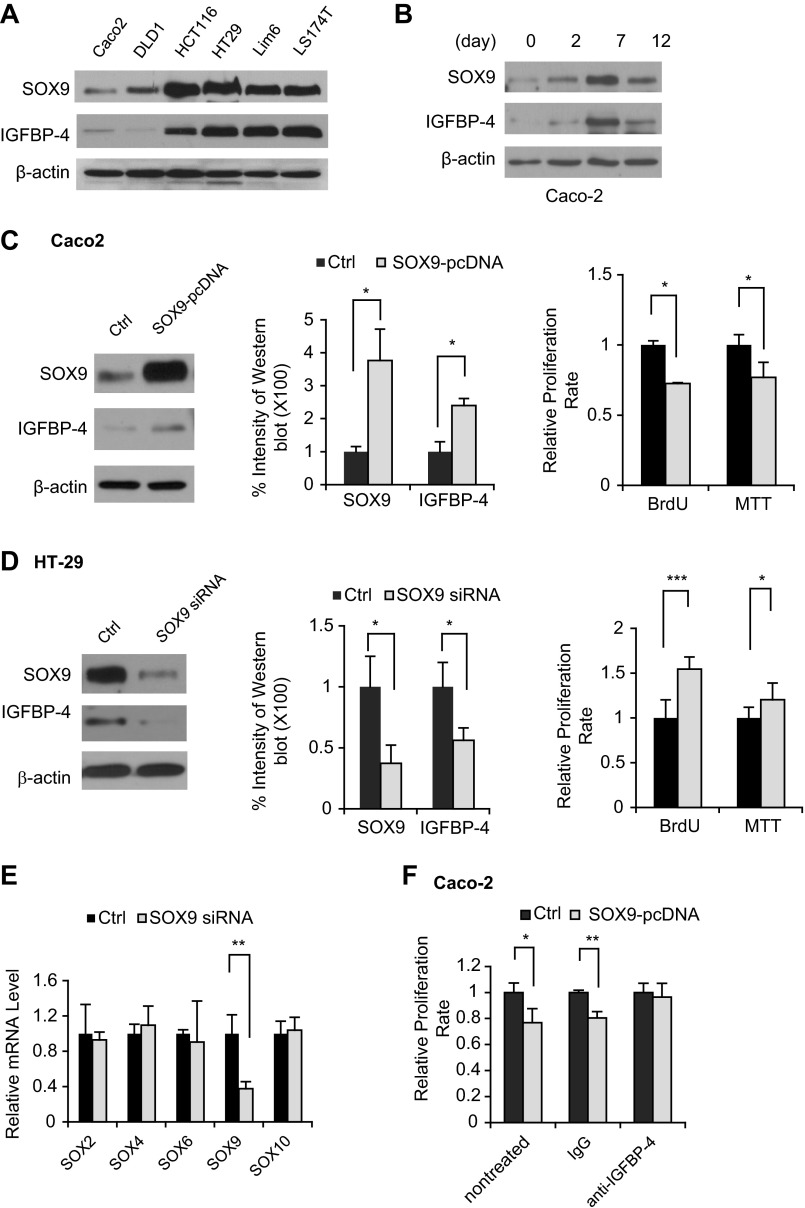
Fig. 4.
Manipulation of SOX9 expression by overexpression or knockdown of SOX9 resulted in altered expression of IGFBP-4. A: Western blots of expression levels of SOX9 and IGFBP-4 in CRC cell lines after overnight culture. B: Western blots of expression levels of SOX9 and IGFBP-4 in cell lysates collected from Caco-2 cells on days 0, 2, 7, and 12 of culture. C and D: Western blot analysis of expression levels of SOX9 and IGFBP-4 (left), quantification of immunoblot bands from 3 repetitions of Western blot experiments (middle), and bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay of cell proliferation after transfection with SOX9-pcDNA in Caco-2 cells or SOX9 small interfering RNA [siRNA, control (Ctrl)] in HT-29 cells (right). E: SOX9 siRNA did not affect expression of any other SOX family transcription factors in the intestine as measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Expression of the SOX family of transcription factors that are known to be expressed in the intestine, including SOX2, SOX4, SOX6, SOX9, and SOX10, was measured by real-time PCR from SOX9 siRNA- and control siRNA-transfected (Ctrl) HT-29 cells. F: reduction of cell proliferation in Caco-2 cells was restored following treatment with a neutralizing antibody against IGFBP-4. Overexpression of SOX9 upregulated IGFBP-4 expression and suppressed cell proliferation in human CRC cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.