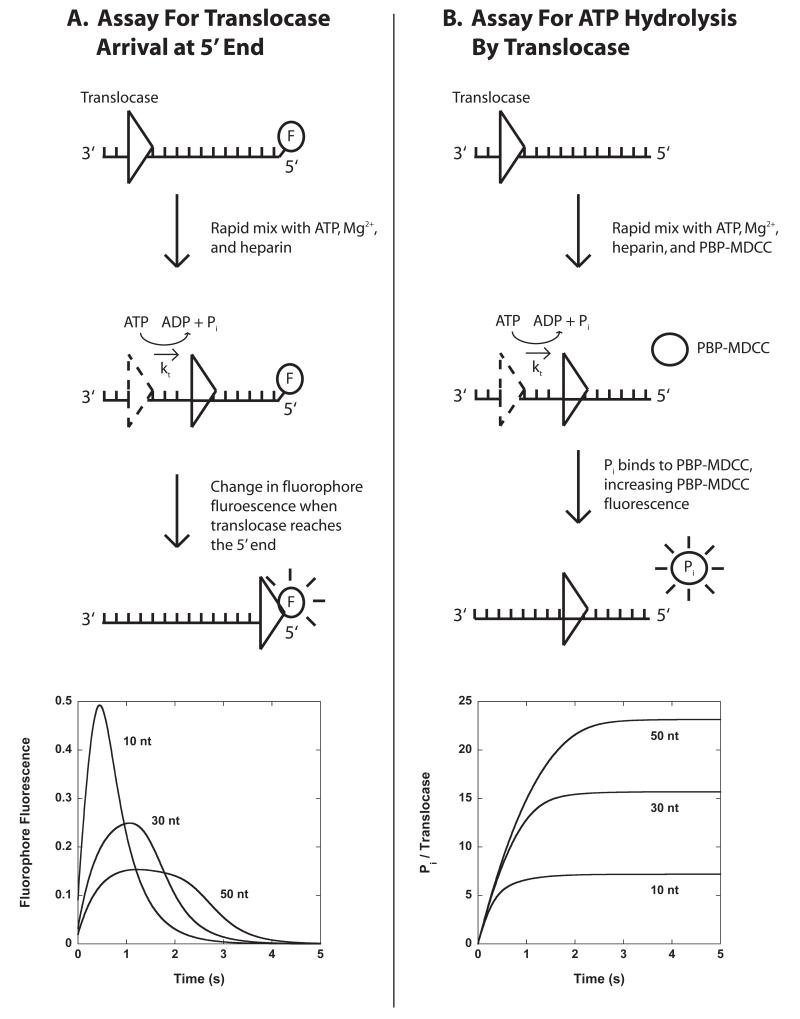
Figure 3.1.
Stopped-flow assays for monitoring the pre-steady state kinetics of enzyme translocation along ssNA. Panel A: A translocase is pre-bound to single-stranded ssNA labeled at the 5′-end with a fluorescent dye, then rapidly mixed with ATP, Mg2+, and heparin (protein trap) to initiate translocation. When the translocase nears the 5′-end of the ssNA the fluorescence of the dye is either quenched or enhanced. Example time courses are shown for three different lengths of DNA. Panel B: A translocase is pre-bound to ssNA and then rapidly mixed with ATP, Mg2+, heparin, and an excess concentration of fluorescently labeled phosphate binding protein (PBP-MDCC) to initiate translocation. As the translocase moves along the filament, ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). PBP-MDCC rapidly binds the Pi resulting in an increase in the PBP-MDCC fluorescence. Example time courses are shown for three different lengths of ssNA.