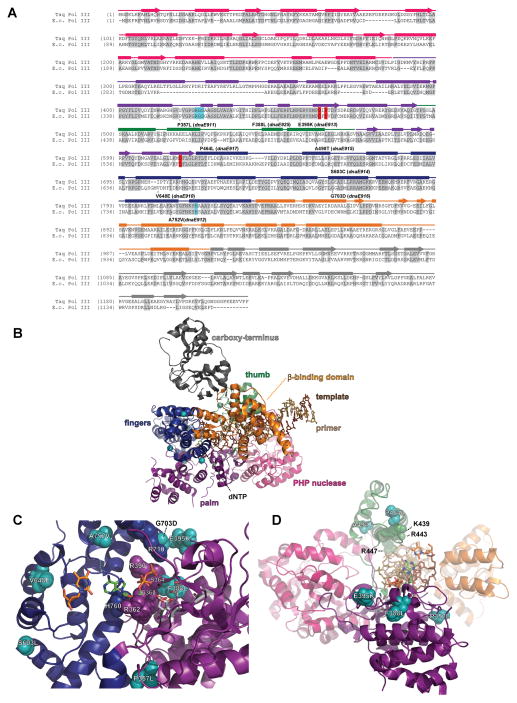
Figure 4.
Pol III antimutators. (A) Alignment of Pol III peptide sequences from Thermus aquaticus (Taq Pol III) and Escherichia coli (E.c. Pol III). Secondary structural elements based on the Taq Pol III structure (Wing et al., 2008) (PDB accession code 3E0D) are indicated below the alignment and color coded to depict their location (PHP, magenta; palm, purple; fingers, blue; thumb, green; β-binding, orange; carboxy-terminus, charcoal): rectangles, α-helices; arrows, β-strands; solid lines, loops. Amino acids shaded in gray are conserved between Taq and E. coli. Aspartates that coordinate metal ions for catalysis are shaded in red. Residues that stack with ribose of incoming dNTP are shaded in cyan. E. coli dnaE amino-acid changes and allele numbers are depicted below the alignment. (B) Distribution of antimutator substitutions. The α-carbons of antimutator positions are shown as teal spheres. (C) Antimutators near the Pol III active site. The RGS motif (362–364) and H760 cradle the incoming dNTP, while R390 and R710 interact with the triphosphate. (D) Antimutators in the Pol III Thumb. A498T and P464L affect the positioning of an α-helix that includes three basic residues that interact with the primer•template backbone (K439, R443, R447). A color version of this figure is available online.