FIG. 2.
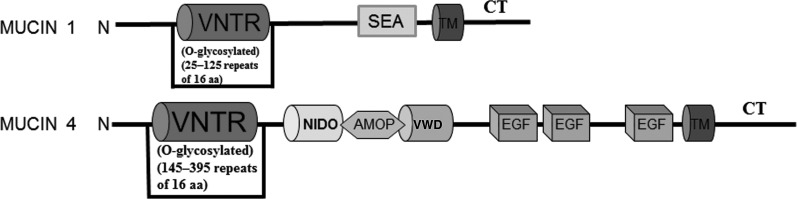
Structural motifs of mucin 1 and mucin 4. Key domains include the following: a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR); sperm protein, exterokinase, and agrin (SEA) modules; transmembrane (TM) domains; cytoplasmic tail (CT); nidogen homology sequence (NIDO); adhesion-associated domain in mucin 4 and other proteins (AMOP); von Willebrand factor D sequence (VWD); and epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like regions. aa, amino acids.
