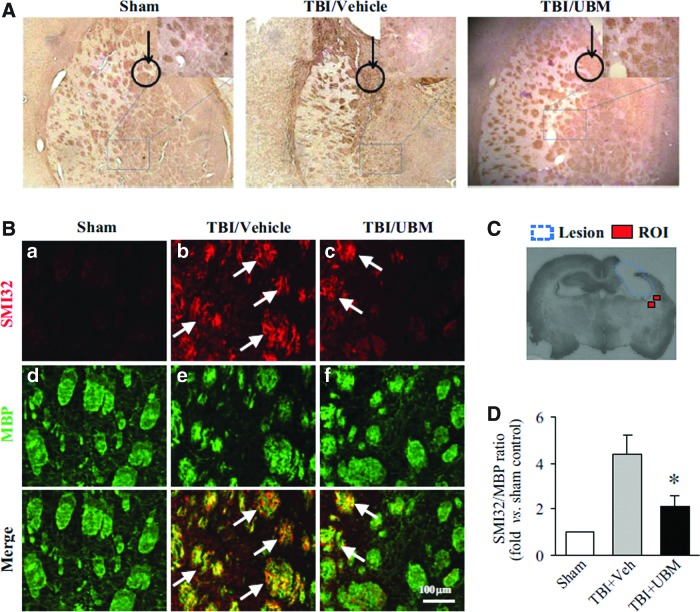
FIG. 3.
UBM treatment attenuates white matter injury in rats following TBI. (A) Staining for the myelin basic protein (MBP) following TBI as an indication of white matter damage revealed that TBI results in a high degree of disorganization of myelin in the rat striatum compared to sham. UBM injection following TBI attenuated the disruption of myelin organization. The black circle with an arrow in each image indicates the implantation position, in the striatum right beneath the CA3 area. The white matter tract underneath the implantation site was observed and shown in the magnified image. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of SMI32 and BMP showed that an increase in SMI32 and a decrease in MBP in rats following TBI compared with sham, but a decrease in SMI32 and an increase in MBP staining was observed in rats treated with UBM compared with treated with vehicle, indicating that UBM injection reduced white matter injury. Arrows indicate the increased SMI132 immunofluorescence in the bundles in the TBI striatum. (C) The location of regions of interest (ROI) in the striatum around lesion are indicated as red squares, where the SM132/MBP ratio was calculated 21 days following TBI. (D) The SMI32/MBP ratio indicates the extent of white matter injury. The relative SMI32/MBP ratio was decreased in rats treated with UBM compared to vehicle treatment. Images are representative of staining for MBP and SMI32 in sham- (n=6), vehicle- (n=12), and UBM-treated (n=10) groups at 21 days after TBI. Data are presented as mean±SE, *p<0.05 versus vehicle or UBM. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea