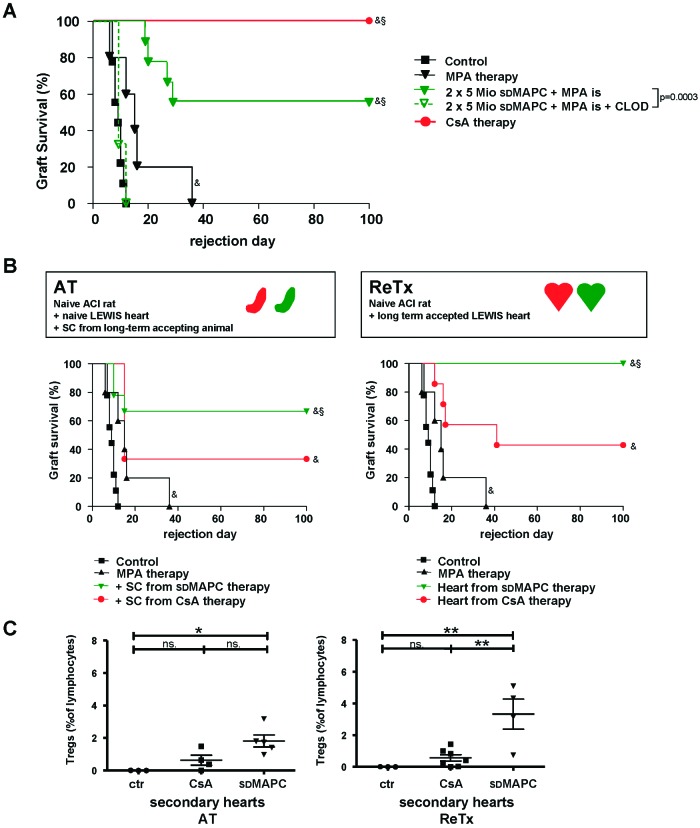
Figure 4.
Allogeneic heart transplantation in the LEW to ACI rat model using third-party multipotent adult progenitor cells (MAPCs). (A): Survival of heart grafts after third-party MAPC infusion. When recipient rats (ACI) received intrasplenic injections of 5 × 106 sdMAPCs on days −4 and 0 plus short-term treatment with MPA followed by allogeneic heart transplantation (LEW heart), allograft survival was prolonged in 60% of recipients (n = 9). When recipient animals that were tolerized through sdMAPCs received monocyte-depleting, clodronate-filled liposomes, all animals rejected the grafts before day 16 (n = 5). 100% of allogeneic grafts from CsA-treated control animals survived (n = 11). (B): When splenocytes from graft-accepting animals were transferred into secondary, naïve recipients, 38% of the secondary grafts survived (n = 8). Splenocytes transferred from MAPC-treated recipients were more effective in this setting, (63%, n = 8). When heart grafts were retransplanted all third-party MAPC-treated grafts survived with no further immunosuppression in secondary recipients (n = 5), whereas the majority of CsA-pretreated grafts were rejected (n = 7). (C): Intragraft lymphocytes isolated from secondary heart grafts that had been subjected to MAPC therapy in the primary recipient contained a significantly larger population of CD4+/CD25+/foxp3-positive cells than control grafts; the grafts subjected to CsA monotherapy did not contain more CD4+/CD25+/foxp3-positive cells than control grafts (representative contour plot and mean percentage of total lymphocytes, at least n = 4 for each group). Statistical comparison of Treg frequencies between three groups was analyzed using analysis of variance, followed by a post test using Bonferroni comparison of all pairs. *, p < .05; **, p < .01. Survival data were compared using the log-rank test: &, p < .05 versus untreated control group; §, p < .05 versus MPA-treated group. Abbreviations: AT, adoptive transfer; CLOD, clodronate-filled; CsA, ciclosporin A; ctr, control; is, intrasplenic; Mio, million; MPA, mycophenolate; ns, not significant; ReTx, retransplantation; SC, splenocytes; sdMAPC, Sprague-Dawley multipotent adult progenitor cell; Tregs, T regulatory cells.