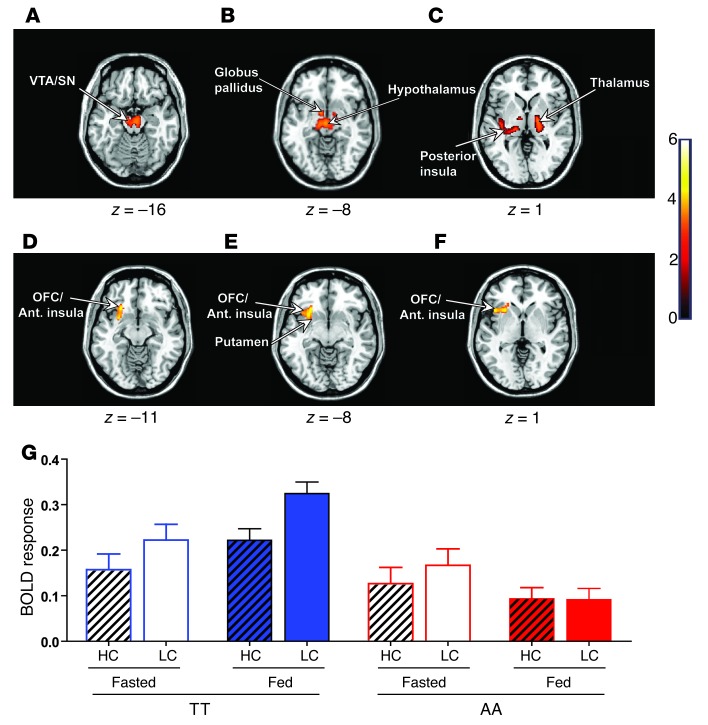
Figure 2. Effect of the FTO rs9939609 genotype on BOLD responses to food and non-food images.
(A–F) Axial slices with superimposed group functional activity. (A–C) Brain regions where the TT and AA genotypes exhibited significantly different BOLD responses while viewing food images (all food greater than non-food) in the fasted state, with TT subjects showing a greater BOLD response than AA subjects. (D–F) Brain regions where a marked interaction between the FTO genotype (TT versus AA) and nutritional state (fed versus fasted) was found in BOLD responses to high-incentive- versus low-incentive-value food images (high-calorie greater than low-calorie). Left side of each panel is the left side of the brain. z is the MNI space z coordinate of the axial slice. T color scale reflects the T value of the functional activity. Results are presented at a threshold of P < 0.05, FWE corrected on the basis of cluster extent. Ant. insula, anterior insula. (G) Mean response (β coefficients) for the left anterior insula/OFC (BA47) cluster displaying genotype-by-nutritional state interaction for the high-calorie versus low-calorie contrast. Graph shows cluster mean parameter estimates ± SEM for high-calorie (hatched bars) and low-calorie food images (bars without hatching) in the fasted (open bars) and fed (solid bars) states in TT (blue bars) and AA (red bars) subjects. HC, high-calorie; LC, low-calorie.