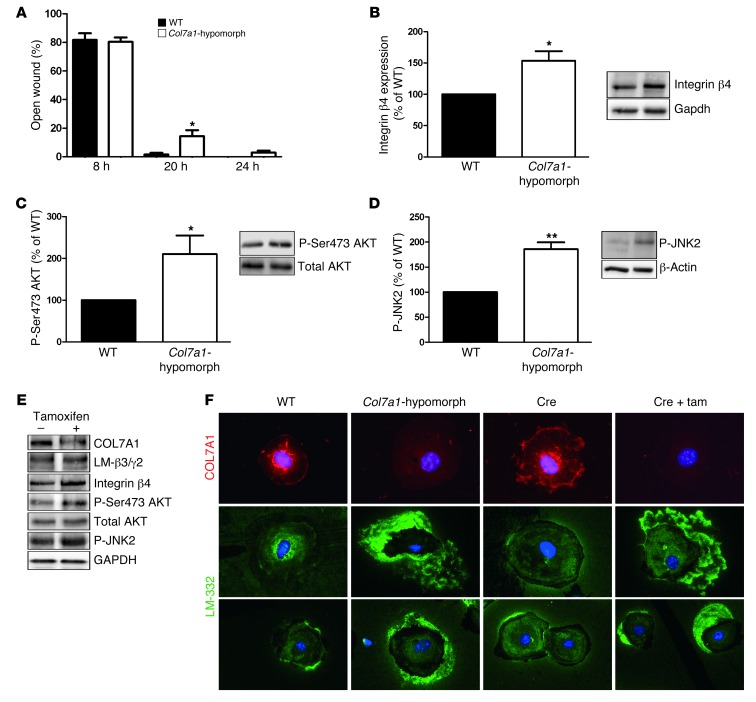
Figure 5. Mechanisms of delayed wound closure in Col7a1-hypomorphic keratinocytes.
(A) In in vitro assays, wound closure by keratinocytes was assessed at 8, 20, and 24 hours. At 20 and 24 hours, Col7a1-hypomorphic keratinocytes closed wounds at a reduced rate. n = 6; values represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. (B–D) Western blotting of wild-type and Col7a1-hypomorphic keratinocyte protein lysates revealed increased expression of integrin β4 subunit (B) and increased phosphorylation of Ser473 AKT (C) and JNK2 (D) in cultured Col7a1-hypomorphic keratinocytes. Densitometric quantification of keratinocyte isolations is also shown. n ≥ 3; values represent mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (E) Western blots on cell lysates from tamoxifen-induced Col7a1 knockout mouse keratinocytes. Keratinocytes from the same isolation were divided into 2 pools: one was treated with 4-OH tamoxifen to induce Col7a1 knockout, the other received only DMSO and served as control. The changes in Col7a1-hypomorphic keratinocytes were replicated in keratinocytes after forced COL7A1 loss. Loss of COL7A1 did not affect expression of laminin-332 (LM-β3/γ2; representing the laminin β3 and γ2 chains of laminin-332), but increased expression of integrin β4 and phosphorylation of Ser473 AKT and JNK2. Total AKT and GAPDH were used to ensure equal loading. (F) Altered Laminin-332 organization in Col7a1-hypomorphic keratinocytes. Primary keratinocytes of the indicated genotypes and treatments were cultured for 24 hours in the presence of ascorbate and stained for COL7A1 (red) and laminin-332 (green). Original magnification, ×400. Tam, tamoxifen.