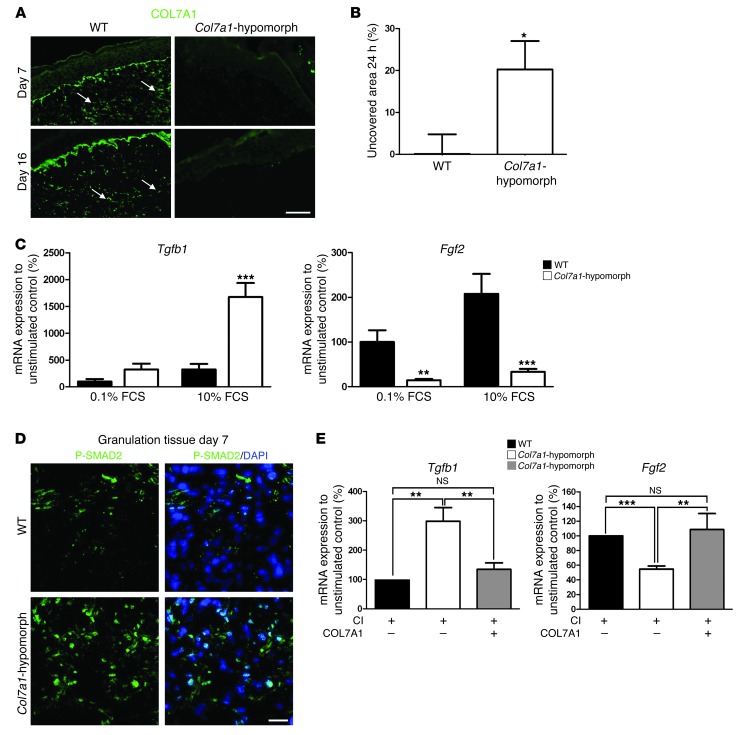
Figure 7. COL7A1 affects dermal fibroblasts during wound healing.
(A) Granulation tissue in 7- and 16-day wounds in wild-type and Col7a1-hypomorphic mice stained for COL7A1 (green). Note the presence of COL7A1 aggregates (arrows) within the healing dermis in wild-type mice. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) In vitro scratch wound assay. Col7a1-hypomorphic fibroblasts closed the scratch wound significantly slower than did wild-type cells. n = 7. (C) Serum-response assay, which replicates fibroblast signaling events during wound healing (26). Dermal fibroblasts were starved in 0.1% FCS for 48 hours, stimulated with 10% serum for 5 hours, and analyzed for gene expression. Tgfb1 and Fgf2 mRNA expression were normalized to Gapdh and a nonstimulated control. Serum stimulation substantially increased Tgfb1 mRNA expression, but reduced Fgf2 expression, in Col7a1-hypomorphic compared with wild-type fibroblasts. n = 5. (D) P-SMAD2 staining (green) of granulation tissue in day-7 wounds confirmed increased activation of TGF-β1 signaling in the Col7a1-hypomorphic wound. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. (E) Supplementation of recombinant COL7A1 to Col7a1-hypomorphic fibroblasts normalized Tgfb1 and Fgf2 expression. Dermal fibroblasts were grown on 1.5 μg collagen I (CI), with or without 1.5 μg/well recombinant COL7A1, until they reached confluence, then serum-starved for 48 hours and stimulated with 10% FCS for 5 hours. mRNA expression was analyzed as in C. n ≥ 4. All values represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.