Figure 3.
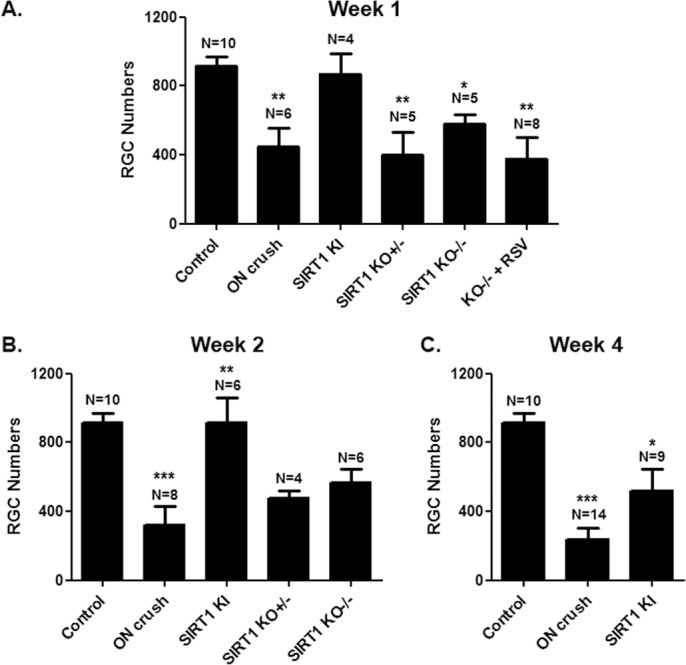
SIRT1 overexpression prevents RGC loss. (A) Mean ± SEM number of RGCs is significantly decreased 1 week post–optic nerve crush as compared with control eyes (**P < 0.01). No loss of RGCs compared with controls occurs 1 week post–optic nerve crush in SIRT1-KI mice, with RGCs numbers significantly higher than eyes from wild-type (**P < 0.01); heterozygous SIRT1-KO (**P < 0.01); or homozygous SIRT1-KO (*P < 0.05) mouse eyes that underwent optic nerve crush. There is no difference in RGC numbers between wild-type and SIRT1-KO optic nerve crush eyes. Daily treatment with 250 mg/kg resveratrol (RSV) failed to prevent RGC loss following optic nerve crush in homozygous SIRT1-KO mice, with RGC numbers decreased compared with controls (**P < 0.01). (B) Two weeks post–optic nerve crush, the number of RGCs is significantly decreased as compared with control eyes (***P < 0.001). No loss of RGCs compared with controls occurs post–optic nerve crush in SIRT1-KI mice, with RGC numbers significantly higher than eyes from wild-type, heterozygous SIRT1-KO, or homozygous SIRT1-KO (**P < 0.01) mouse eyes that underwent optic nerve crush. There is no difference in RGC numbers between wild-type and SIRT1-KO optic nerve crush eyes. (C) Four weeks post–optic nerve crush, RGC numbers are significantly decreased compared with control eyes (***P < 0.001) and with SIRT1-KI optic nerve crush eyes (*P < 0.05).
