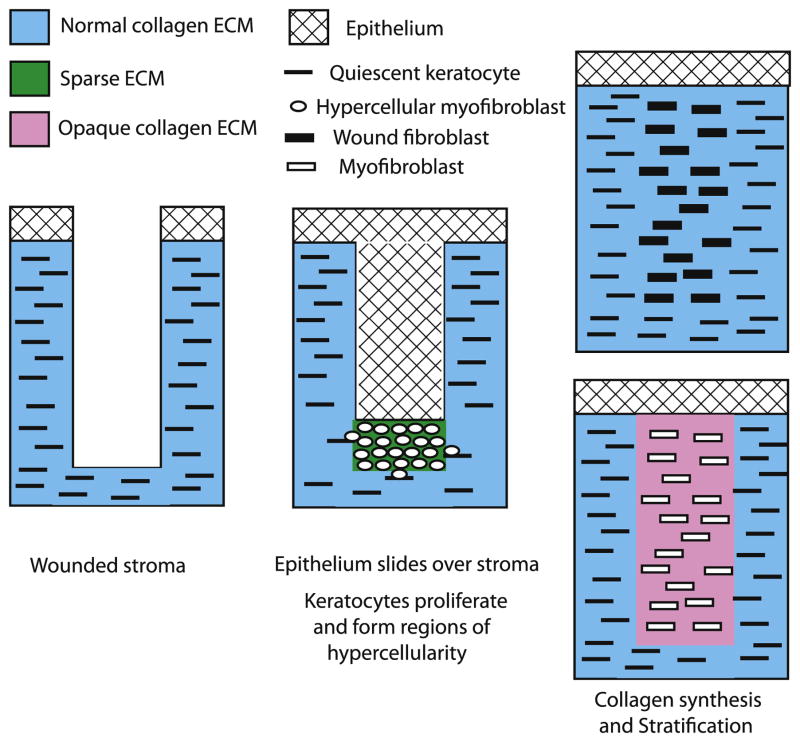
Figure 5.
Healing in a corneal stromal incisional wound. The corneal epithelium loses it hemidesmosome attachment to the basement membrane and migrates over the wound site. The quiescent keratocytes are activated to proliferate and produce α smooth muscle actin but synthesize only low levels of ECM. The resulting hypercellular myofibroblasts accumulate in regions under the epithelium. The hypercellular myofibroblasts then become either wound fibroblasts that produce a normal collagen fibril containing ECM that restores transparency or become myofibroblasts that produce a light-scattering collagen fibril containing ECM that is opaque.