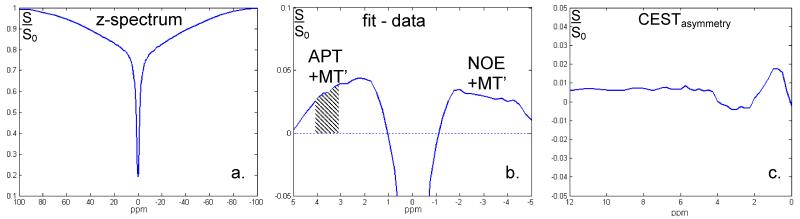
Figure 5.
Results of z-spectrum (a) averaged over the glandular tissue of one subject. After subtraction of the spectrum from its Lorentzian fit (from −5 to 9 ppm), positive signals on both sides of the water resonance can be seen reflecting, apart from a small contribution of MT (MT’), APT (shaded area) and NOE effects respectively (b). The asymmetry with respect to the water resonance is less than 1%, with an observable dip around 3.5 ppm (c). Note though that dynamically changing susceptibility effects during the acquisition of the CEST spectrum can reduce the spectral resolution, the stability of detection remains high as can be observed in the close to 0.1% noise in the CEST asymmetry spectrum (c).