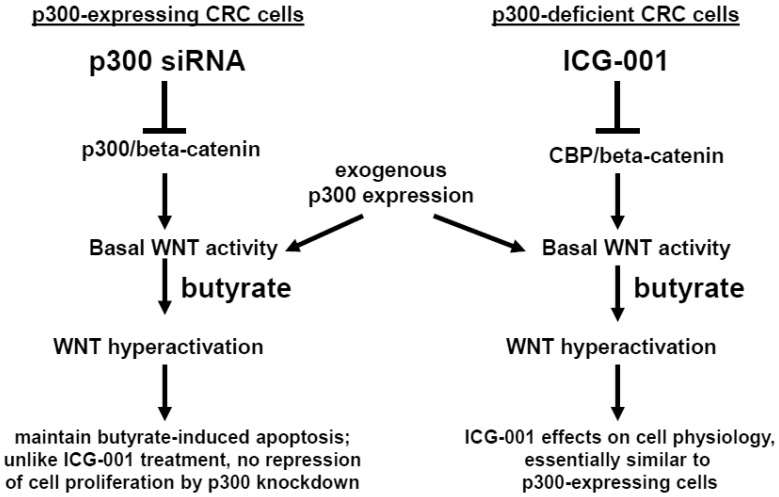
Fig 7.
Role of p300 in mediating the effects of butyrate on WNT signaling in CRC cells. (Left). In p300-expressing CRC cells (e.g., HCT-116 and SW620), p300-mediated WNT/catenin activity, which is repressed by p300 siRNA knockdown, contributes to WNT hyperactivation by butyrate. However, butyrate-mediated apoptosis, which is in part dependent on WNT signaling 29, is maintained in cells exposed to p300 siRNA. Exogenous (over)expression of p300 stimulates WNT/catenin activity and WNT hyperactivation in HCT-116, but not SW620, CRC cells. (Right). Previous reports have suggested that ICG-001, which represses CBP-mediated WNT signaling, works in part by inhibiting CBP/beta-catenin association and promoting p300/beta-catenin association 23-28. However, in the present study, we show that p300 expression is not required for the activity of ICG-001 on basal and butyrate-induced WNT/catenin activity, as demonstrated in the p300-deficient CRC cell lines HCT-R and HCT-15. Exogenous expression of p300 in these cell lines stimulates WNT/catenin activity and WNT hyperactivation. The effects of exogenous p300 expression on WNT signaling can in some cases be inhibited by the CBP-specific inhibitor ICG-001 by as yet unknown mechanisms. Arrows indicate positive interactions (activation); blocked lines indicate negative interactions (repression).