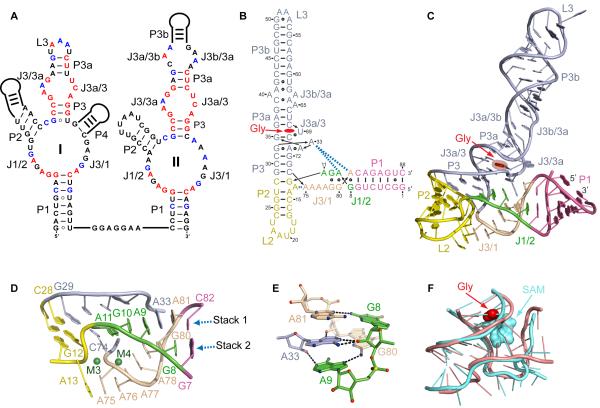
Figure 1. Sequence and Structure of the V. cholerae Riboswitch.
(A) Secondary structure schematics of the glycine riboswitch with tandem sensing domain arrangement. Nucleotides conserved in ≥95 and ≥75 % sequences are in red and blue, respectively.
(B) Crystal structure-based schematic of the VCII RNA fold. The bound glycine is in red. Dashes and circles indicate Watson-Crick and non-canonical base pairs. Key tertiary stacking interactions are shown as blue dashed lines.
(C) Overall crystal structure of VCII RNA in a ribbon representation.
(D) Zoomed-in view of the three-way junction. Green spheres depict Mg2+ cations.
(E) Intercalation of A33 into the junctional region. The RNA is shown in stick representation with color scheme of atoms (nitrogen in blue, oxygen in red, phosphorus in yellow, and carbon in arbitrary colors). Putative hydrogen bonds are shown with black dashed lines.
(F) Superposition of the three-way and four-way junctions of the glycine (light pink) and SAM-I (light blue) riboswitches, respectively. The root mean square deviation (RMSD) is 1.48 Å.