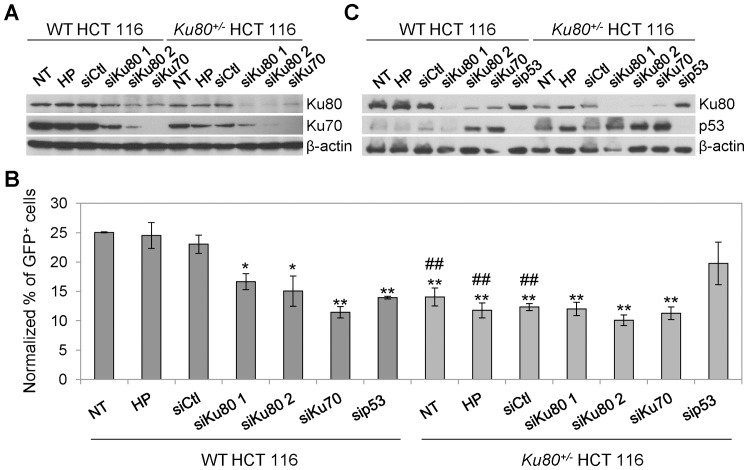
Figure 3. HIV-1-driven GFP expression in WT HCT 116 cells is decreased by transient depletion of Ku.
(A–C) Wild-type (WT) and Ku80+/− human colon carcinoma HCT 116 cells were transfected with an unrelated sequence (siCtl) or with siRNAs directed against Ku80 (siKu80 1 or 2), Ku70 (siKu70) or p53 (sip53). Seventy-two hours later, the protein levels of Ku80 and Ku70 (A) or Ku80 and p53 (C) were assessed by Western-blot analysis. Actin levels were monitored to ensure equal loading of lanes. Alternatively, 72 h upon transfection, the cells were transduced with XCD3 (HIV-1 env- nef - IRES-gfp) at low m.o.i. (<0.3) for additional 48 h followed by cytofluorimetric assessment of green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression (B). NT (non-transfected) and HP (Hiperfect®) correspond to cells kept in control condition or exposed to the same amount of liposomes as used for transfection but in the absence of siRNA, respectively. In (B), the percentages of GFP-positive (GFP+) cells were normalized to the total viral DNA content per cell as determined by quantitative PCR (Q-PCR) 24 h after transduction. The results obtained from at least 3 independent experiments were then normalized to a GFP expression level of 25% (of note, the level of GFP expression of NT, HP or siCtl WT cells before normalization was always comprised between 20 and 30%). The results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01 as compared to HP and siCtl-transfected WT cells; #, p<0.05 and ##, p<0.01 as compared to WT cells subjected to the same transfection condition.