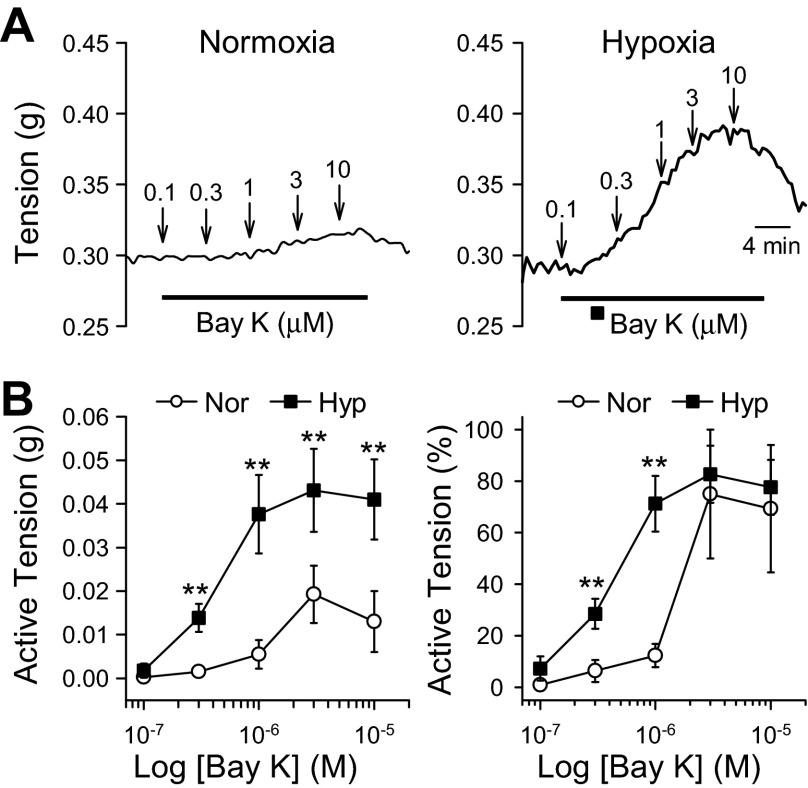
Fig. 5.
Chronic hypoxia enhances Bay K8644-mediated pulmonary vasoconstriction. A: representative tracings showing isometric tension before, during, and after application of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (VDCC) agonist Bay K8644 (0.1–10 μM) in isolated pulmonary arterial rings from mice exposed to normoxia and hypoxia (for 4 wk). B: summarized data (means ± SE) showing the dose-response curves of Bay K8644-induced active tension (depicted as increase in absolute active tension, left, and tension increase normalized to the maximal tension) in PA rings isolated from Nor (open circles, n = 4) and Hyp (solid squares, n = 8) mice. **P < 0.01, vs. Nor.