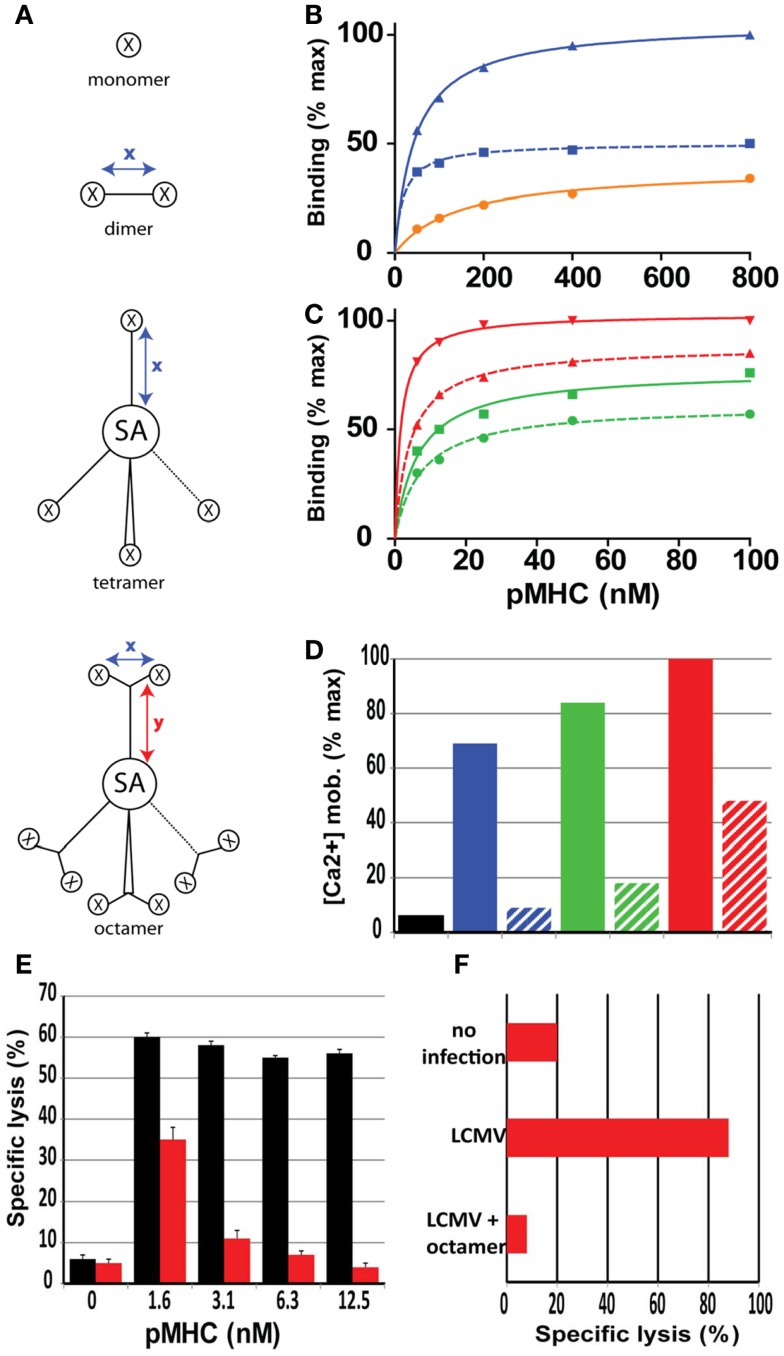
Figure 2.
Role of valence and spacer distances of soluble pMHC complexes on binding and activation of CD8+ T cells. (A) Cartoons of mono, di, tetra, and octamer pMHC complexes, in which x and y indicate maximal spacer distances in Å, X a pMHC monomer and SA streptavidin. The spacer distances for the pMHC dimers varies from 18 to 90 Å. (B) Relative binding on CD8+ T cells of monomer (black), short dimer (blue), and long dimer (dotted blue). (C) Same as (B) with short tetramer (green), long tetramer (dotted green), short octamer (red), and long octamer (dotted red). Short distances are<20 Å and long distances are>80 Å. (D) Relative activation (Ca2+ mobilization) of CD8+ T cells after binding of the represented pMHC complexes. (E) Specific lysis of target cells (GP33 peptide sensitized P815/Db cells) was assessed following incubation with LCMV d8 CD8+ CTL in the presence of Db/GP33 monomer (black bars) or Db/GP33 long octamer (red bars). (F) Specific lysis of GP33 peptide sensitized P815/Db cells was assessed in LCMV infected mice that were or were not (LCMV) injected previously with octamer. Presented data were derived from Ref. (36–38).