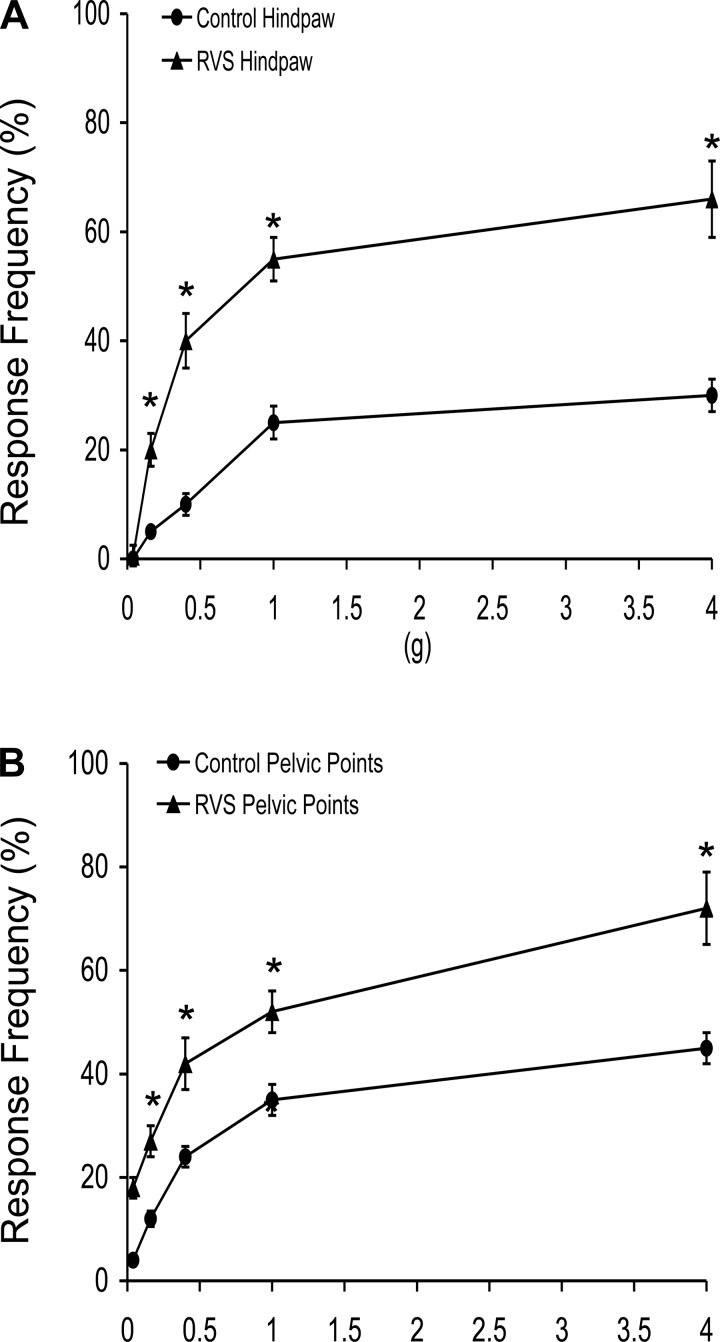
Fig. 3.
Somatic sensitivity testing of the hindpaw and pelvic regions with von Frey hairs in control (circles) rats and rats exposed to 7 days of RVS (triangles). The von Frey hairs were applied in an up-down method for 1–3 s with an interstimulus interval of 15 s. For pelvic region stimulation, stimulation was confined to the lower abdominal area overlying the urinary bladder. The following behaviors were considered positive responses to pelvic region stimulation: sharp retraction of the abdomen, jumping, or immediate licking or scratching of the pelvic area. A positive response to hindpaw stimulation was sharp withdrawal of the paw or licking of the tested hindpaw. Rats exposed to 7 days of RVS had a significantly (*P ≤ 0.01) increased hindpaw response frequency (A) and pelvic response frequency (B) with all von Frey hairs (0.1–4 g) tested compared with control rats (no RVS). Hindpaw or pelvic sensitivity testing with calibrated von Frey hairs was determined in separate groups of rats. All somatic testing was performed in a blinded manner with respect to treatment. Values are means ± SE. Sample sizes are n of 8; *P ≤ 0.01.