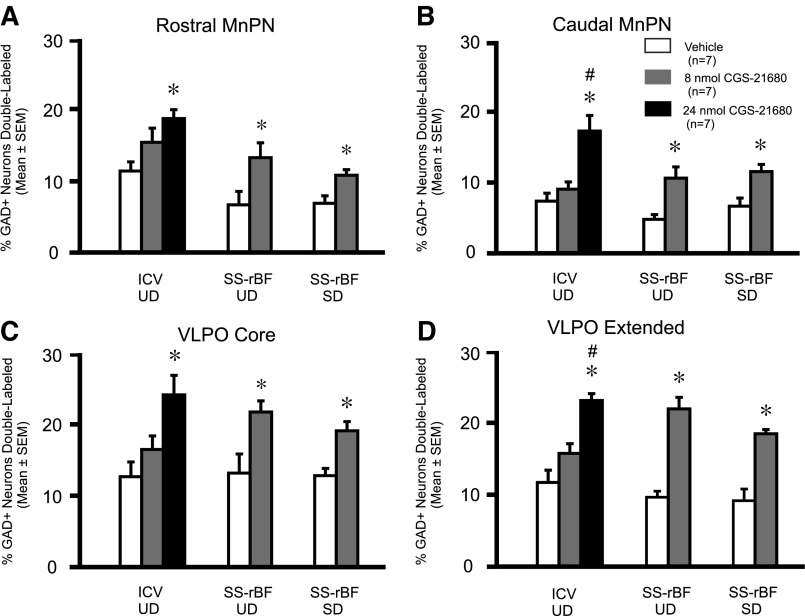
Fig. 4.
Effects of CGS-21680 on Fos-IR in MnPN and VLPO GABAergic neurons. Effects of CGS-21680 on the percentage of GAD+ neurons expressing Fos-IR (%GAD+ neurons double-labeled) in the MnPN (A and B) and VLPO (C and D) after intracerebroventricular or SS-rBF injections in undisturbed (UD) animals and after SS-rBF injections in animals that were sleep-deprived (SD) for 2 h after drug or vehicle administration. In UD animals, both ICV and SS-rBF injections of CGS-21680 increased the percentage of GAD+ neurons expressing Fos-IR in all of the preoptic area (POA) subregions examined; rostral MnPN (ICV: F2,18 = 5.66, P = 0.012; SS-rBF: t = −2.35, P = 0.037), caudal MnPN (ICV: F2,18 = 11.75, P = <0.001; SS-rBF: t = −3.37, P = 0.006), core VLPO (ICV: F2,18 = 6.69, P = 0.007; SS-rBF: t = −2.76, P = 0.017), and extended VLPO (ICV: F2,18 = 17.63, P = <0.001; SS-rBF: t = −6.78, P = <0.001). Like UD animals, CGS-21680 injection into the SS-rBF in SD animals also increased Fos-IR in GAD+ neurons in all of the POA-subregions examined (rostral MnPN: t = −2.98; P = 0.011; caudal MnPN: t = −3.19; P = 0.008; core VLPO: t = −3.83; P = 0.002; extended VLPO: t = −5.40; P = <0.001). *Significantly different from vehicle, P < 0.05. #Significantly different from 8 nmol, P < 0.05.