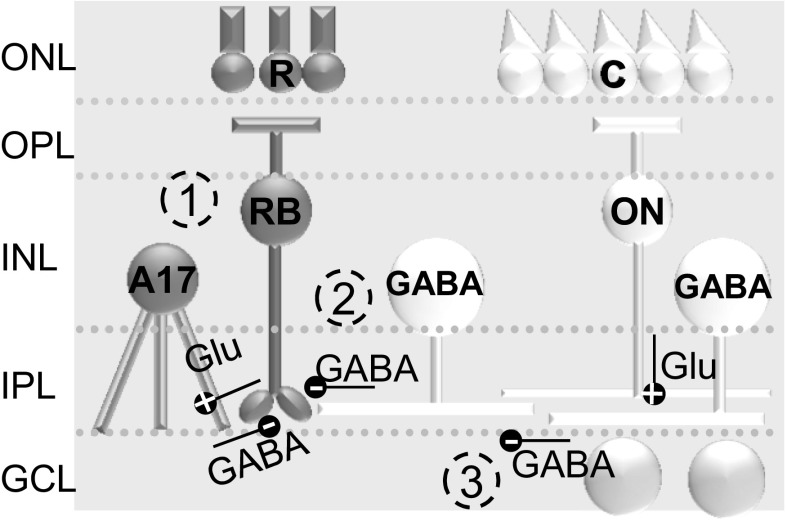
Fig. 1.
Potential pathways of rod bipolar cell (BC) inhibition. 1) In dark-adapted retinas where rod (R) pathways are active, rod BCs (RB) activate A17 amacrine cells (ACs) (+, glutamate) and receive significant GABAergic feedback inhibition (−, GABA) from those A17 ACs (dark gray pathway). 2) They also receive a small amount of glycinergic inhibition (not shown here) and GABAergic inhibition (−) that comes from cone (C)-activated pathways, activated (+) by ON cone BCs (ON). 3) Input from GABAergic ACs onto rod BCs is modulated by GABAA receptor-mediated serial connections between GABAergic ACs. ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer.