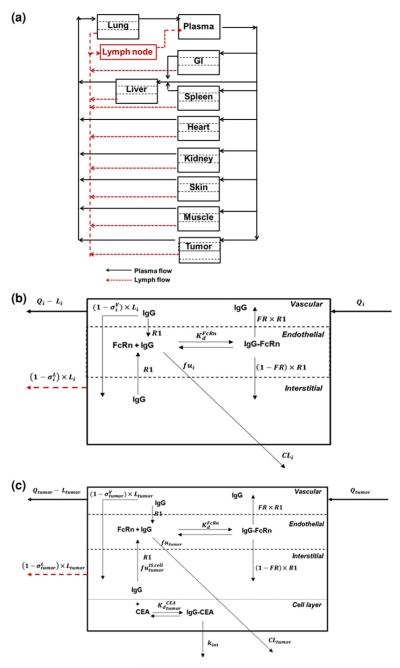
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of the PBPK model of mAb disposition. a System Model: The plasma and lymphatic flow to and from each organ are presented by solid and dashed arrows. Each tissue within this model is divided into vascular, endosomal and interstitial sub-compartments. b Organ Model: Qi and Li are the plasma and lymph flow rates, R1 is the endosomal uptake and recycling rate constant for IgG, FR is the fraction of recycled antibody that is transported to the vascular compartment. The vascular and lymph reflection coefficients are and is IgG-FcRn equilibrium dissociation constant. CLi represents the rate of organ specific clearance of unbound IgG, and fui is the unbound fraction of IgG within the endosomal compartment. To allow for anti-cancer antibody interaction with cellular antigens, an additional cellular sub-compartment was assumed for tumor. c Tumor model: The model assumes equilibrium binding kinetics between T84.66 in the interstitial space and cellular CEA. The fraction of IgG not bound to CEA is , and the T84.66-CEA complex degrades irreversibly by the internalization rate constant, kint. The total T84.66 concentration in each tissue was based on the sum of the total antibody amount in each sub-compartment and divided by the weight of each organ. For the tumor compartment, the total tumor weight increased as a function of time, based on the growth rate of the tumor