Figure 3.
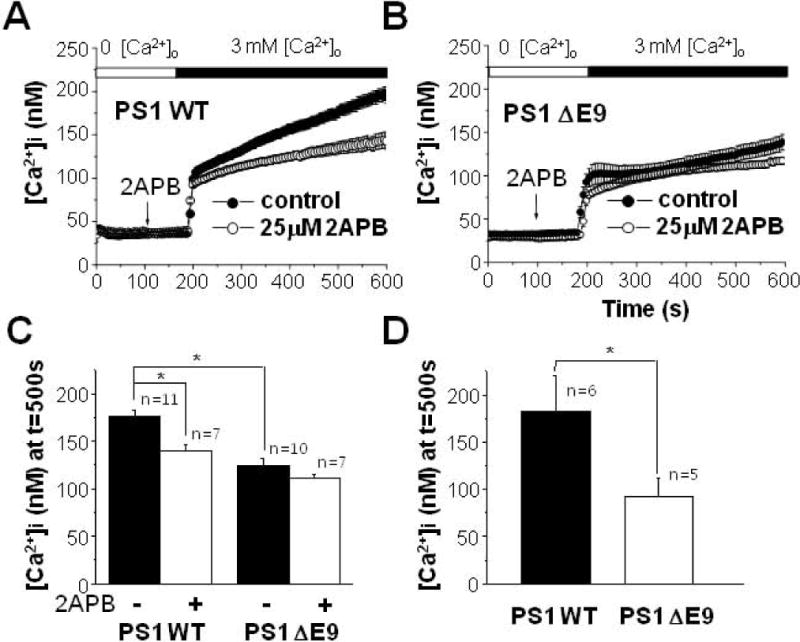
Effect of 2APB on Ca2+ influx following the depletion of extracellular Ca2+ in PS1 WT and PS1 ΔE9 cells. (A) PS1 WT cells were pre-treated either with (n = 7) or without (n = 11) 25 μM 2APB for 100 s in Ca2+-free solution. Then, [Ca2+]i was measured by adding back 3 mM Ca2+ into extracelluar solution. 2APB was able to block some component of Ca2+ influx only in PS1 WT cells. (B) Similarly, PS1 ΔE9 cells were pre-treated either with (n = 7) or without (n = 10) 25 μM 2APB before [Ca2+]i was measured by adding back 3 mM Ca2+ into extracelluar solution. 2APB was not able to block Ca2+ influx. (C) The effects of 2APB on Ca2+ influx were compared between PS1 WT and PS1 ΔE9 cells. (D) The effects of γ-secretase inhibitor on Ca2+ influx following the depletion of extracellular Ca2+. PS1 WT (n = 6) and PS1 ΔE9 cells (n = 5) were pre-treated with 100 nM compound E for 8 h before measuring Ca2+ influx by adding back 3 mM Ca2+ into extracelluar solution. * represents p < 0.05 from paired t-tests.
