Figure 1.
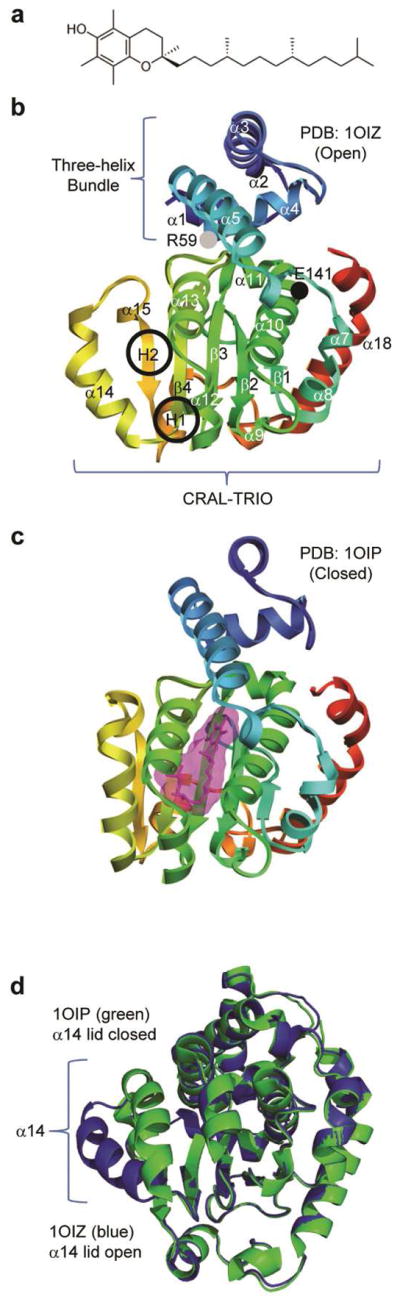
Molecular structures of vitamin E and the different forms of α-TTP. (a) RRR-α-tocopherol (vitamin E). (b) In the unbound structure (PDB code: 1OIZ), a ‘lid’ formed by the α14 region is open, allowing entrance to a hydrophobic binding pocket. The CRAL-TRIO domain is indicated in brackets. The black and gray circles indicate the E141K and R59W mutation regions, respectively. The two hinge regions are circled and labeled as H1 and H2. (c) In the bound conformation (PDB code: 1OIP), the lid is closed, enclosing the binding pocket. (d) 1OIZ (blue) and 1OIP (green) overlaid and aligned by Cα RMSD. The Cα RMSD between the two structures excluding α14 was 0.5 Å
