FIGURE 1:
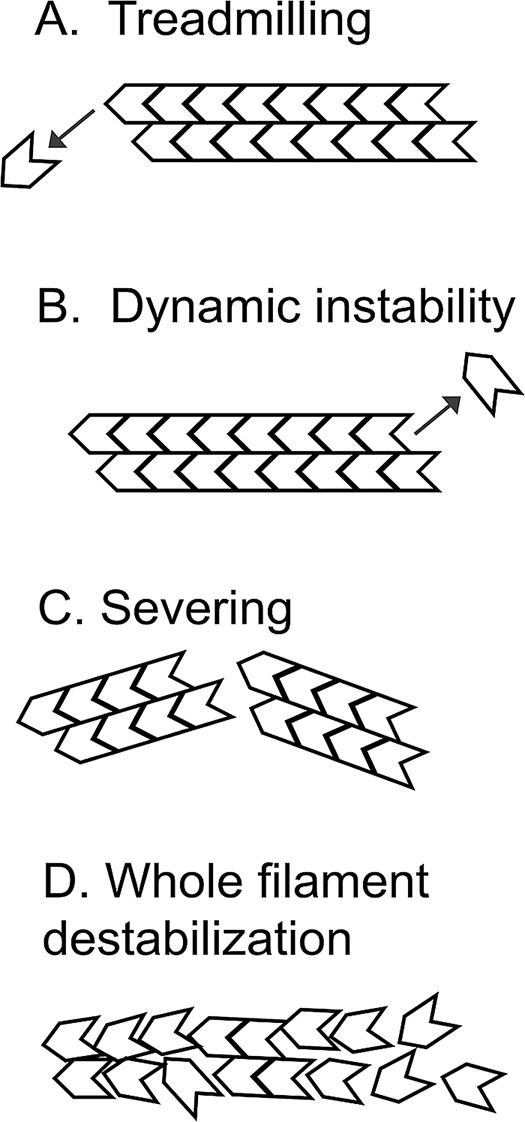
Alternative modes of actin disassembly. (A) Treadmilling filaments lose actin subunits from the pointed ends of filaments. Pure actin treadmills at steady state, which is a popular model for describing actin turnover in cells. (B) Dynamic instability would occur if ATP hydrolysis were to convert the barbed end from one that grows to one that shrinks. Microtubules and prokaryotic ParM filaments undergo dynamic instability, but dynamic instability has not been seen with actin. (C) Severing cuts a filament to produce two daughter filaments without loss of polymer mass. Cofilin severs actin filaments in vitro. (D) Whole-filament destabilization proposes a highly cooperative process in which long stretches of polymer abruptly convert to monomer. Whole-filament destabilization might describe actin disassembly in the presence of cofilin, coronin, and Aip1.
