FIGURE 8:
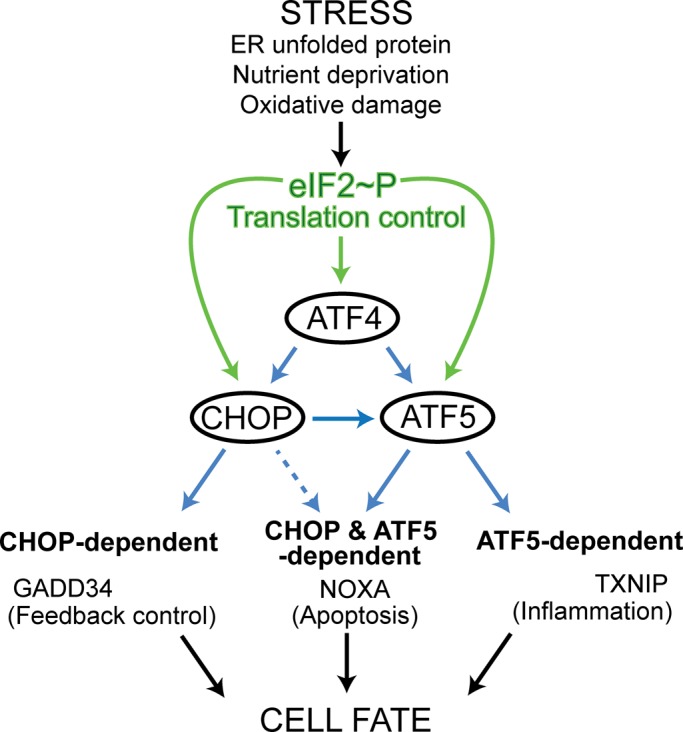
The ISR features a network of ATF4, CHOP, and ATF5 transcription factors in a feedforward loop that controls cell fate. Different stress conditions that disrupt protein homeostasis induce phosphorylation of eIF2, leading to enhanced expression of the bZIP transcription factors ATF4, CHOP, and ATF5 through increased translation, as indicated by the green arrows. ATF4 and CHOP bind the ATF5 promoter and serve to enhance the transcription of ATF5, and CHOP and ATF5, individually or in combination, induce the transcription of target genes (blue arrows). These target gene products affect feedback control, apoptosis, and inflammation, which together can determine cell fate. ATF4 may also serve as a direct contributor to the transcription of some of these target genes, as illustrated by the finding that ATF4, as well as CHOP, can directly bind to the GADD34 promoter to promote transcription (Ma and Hendershot, 2003; Marciniak et al., 2004; Kilberg et al., 2012).
