Figure 4.
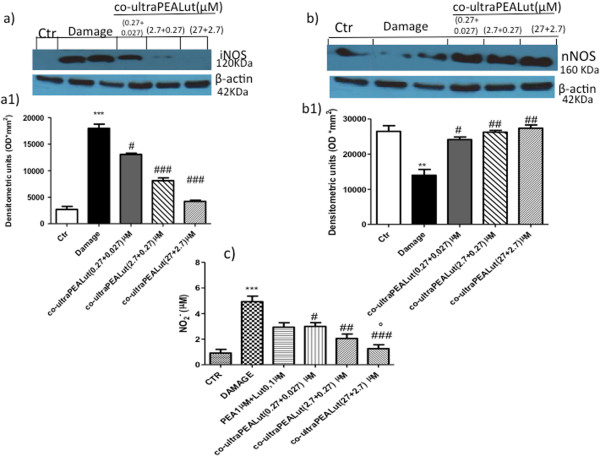
Effect of co-ultraPEALut treatment on iNOS, nNOS and nitrite concentration. iNOS expression was evaluated by western blot analysis in the spinal cord organotypic cultures, collected 24 hours after injury. (a, a1) iNOS expression was significantly elevated in the injured group compared to the control group. On the contrary, iNOS expression was also significantly reduced by pretreatment of co-ultraPEALut at the three different concentrations. This figure is representative of at least three experiments performed on different experimental days. ***P <0.001 versus Ctr; #P <0.05 and ###P <0.001 versus Damage. We also evaluated nNOS expression by western blot analysis, which was significantly reduced by damage. (b, b1) Co-ultraPEALut treatments significantly restored the expression of nNOS. **P <0.01 versus Ctr; #P <0.05 and ##P< 0.01 versus Damage. Moreover, we evaluated the nitrite formation by nitrite assay on medium. (c) An increased formation of nitrite levels was evident in the injured group, while the pretreatment with co-ultraPEALut decreased the injury-induced NO production; indeed, the pretreatment with PEA + Lut association (given as combination therapy) was not able to reduce the increased NO formation as well as the treatment with PEA and with Lut administered alone (data not shown). ***P <0.001 versus Ctr; #P < 0.05, ##P <0.01 and ###P <0.001 versus Damage; °P <0.01 versus PEA 1 μM + Lut 0.1 μM. Ctr, control; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; Lut, luteolin; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; PEA, palmitoylethanolamide.
